Heat shock protein 70 surface-positive tumor exosomes stimulate migratory and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells
- PMID: 15958569
- PMCID: PMC1785299
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3804
Heat shock protein 70 surface-positive tumor exosomes stimulate migratory and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells
Abstract
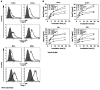
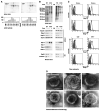
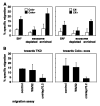
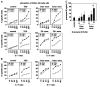
Detergent-soluble membrane vesicles are actively released by human pancreas (Colo-/Colo+) and colon (CX-/CX+) carcinoma sublines, differing in their capacity to present heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70)/Bag-4 on their plasma membranes. Floating properties, acetylcholine esterase activity, and protein composition characterized them as exosomes. An enrichment of Rab-4 documented their intracellular transport route from early endosomes to the plasma membrane. After solubilization, comparable amounts of cytosolic proteins, including tubulin, Hsp70, Hsc70, and Bag-4, but not ER-residing Grp94 and calnexin, were detectable in tumor-derived exosomes. However, with respect to the exosomal surface, only Colo+/CX+ but not Colo-/CX- derived exosomes were Hsp70 membrane positive. Therefore, concomitant with an up-regulated cell surface density of activation markers, migration and Hsp70 reactivity of natural killer (NK) cells was stimulated selectively by Hsp70/Bag-4 surface-positive exosomes, but not by their negative counterparts and tumor cell lysates. Moreover, the exosome-mediated lytic activity of NK cells was blockable by Hsp70-specific antibody. As already shown for TKD stimulation, NK cells preincubated with Hsp70 surface-positive exosomes initiated apoptosis in tumors through granzyme B release. In summary, our data provide an explanation how Hsp70 reactivity in NK cells is induced by tumor-derived exosomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual function of membrane-bound heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), Bag-4, and Hsp40: protection against radiation-induced effects and target structure for natural killer cells.Cell Death Differ. 2005 Jan;12(1):38-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401510. Cell Death Differ. 2005. PMID: 15592361
-
Treatment of colon and lung cancer patients with ex vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells: a clinical phase i trial.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 1;10(11):3699-707. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0683. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15173076 Clinical Trial.
-
The cell surface-localized heat shock protein 70 epitope TKD induces migration and cytolytic activity selectively in human NK cells.J Immunol. 2004 Jan 15;172(2):972-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.972. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14707070
-
Immunostimulatory functions of membrane-bound and exported heat shock protein 70.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2005;11:17-33. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16385841 Review.
-
The role of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) in radiation-induced immunomodulation.Cancer Lett. 2015 Nov 28;368(2):179-84. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25681671 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of exosomes in tumour immunity under radiotherapy: eliciting abscopal effects?Biomark Res. 2021 Mar 31;9(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00277-w. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 33789758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of extracellular vesicle-associated proteins in the progression, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01294-6. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39227992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medulloblastoma exosome proteomics yield functional roles for extracellular vesicles.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042064. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848702 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-106b-5p derived from melanoma cell promotes primary melanocytes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting EphA4.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 19;40(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01906-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33741023 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression.Nat Immunol. 2021 May;22(5):560-570. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00899-0. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33753940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science. 2002;295:1852–8. - PubMed
-
- Multhoff G, Botzler C, Wiesnet M, et al. A stress-inducible 72-kDa heat-shock protein (HSP72) is expressed on the surface of human tumor cells, but not on normal cells. Int J Cancer. 1995;61:272–9. - PubMed
-
- Shin BK, Wang H, Yim AM, et al. Global profiling of the cell surface proteome of cancer cells uncovers an abundance of proteins with chaperone function. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:7607–16. - PubMed
-
- Barreto A, Gonzalez JM, Kabingu E, Asea A, Fiorentino S. Stress-induced release of HSC70 from human tumors. Cell Immunol. 2003;222:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Broquet AH, Thomas G, Masliah J, Trugnan G, Bachelet M. Expression of the molecular chaperone Hsp70 in detergent-resistant microdomains correlates with its membrane delivery and release. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:21601–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

