Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 2A regulates B-cell receptor-induced apoptosis and EBV reactivation through tyrosine phosphorylation
- PMID: 15956608
- PMCID: PMC1143726
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.13.8655-8660.2005
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 2A regulates B-cell receptor-induced apoptosis and EBV reactivation through tyrosine phosphorylation
Abstract
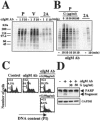
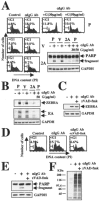
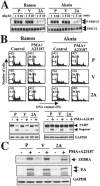
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a human herpesvirus that establishes a lifelong latent infection of B cells. Within the immune system, apoptosis is a central mechanism in normal lymphocyte homeostasis both during early lymphocyte development and in response to antigenic stimuli. In this study, we found that latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) inhibited B-cell receptor (BCR)-induced apoptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases, blocked BCR-induced apoptosis and EBV reactivation in the cells. These findings indicate that LMP2A blocks BCR-induced cell apoptosis and EBV reactivation through the inhibition of activation of tyrosine kinases by BCR cross-linking.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein 2A (LMP2A)-mediated changes in Fas expression and Fas-dependent apoptosis: Role of Lyn/Syk activation.Cell Immunol. 2015 Oct;297(2):108-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Cell Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26255694 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus coopts lipid rafts to block the signaling and antigen transport functions of the BCR.Immunity. 2001 Jan;14(1):57-67. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00089-9. Immunity. 2001. PMID: 11163230
-
Tyrosines 60, 64, and 101 of Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A are not essential for blocking B cell signal transduction.Virology. 1999 Oct 25;263(2):485-95. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9964. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10544120
-
Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP2A regulates reactivation from latency by negatively regulating tyrosine kinases involved in sIg-mediated signal transduction.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):128-36. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7812651 Review.
-
The effects of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A on B cell function.Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20(6):805-35. doi: 10.3109/08830180109045591. Int Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11913951 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A imposes sensitivity to apoptosis.J Gen Virol. 2010 Sep;91(Pt 9):2197-202. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.021444-0. Epub 2010 May 19. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 20484564 Free PMC article.
-
K1 and K15 of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Are Partial Functional Homologues of Latent Membrane Protein 2A of Epstein-Barr Virus.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7248-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00839-15. Epub 2015 May 6. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25948739 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediates transformation through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3-K/Akt Pathway.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9299-306. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00537-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17582000 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases the number of side population stem-like cancer cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jun 3;6(6):e1000940. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000940. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20532215 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma: a role for latent membrane protein 2A.Cell Cycle. 2010 Mar 1;9(5):901-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.5.10840. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20160479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An, S., and K. A. Knox. 1996. Ligation of CD40 rescues Ramos-Burkitt lymphoma B cells from calcium ionophore- and antigen receptor-triggered apoptosis by inhibiting activation of the cysteine protease CPP32/Yama and cleavage of its substrate PARP. FEBS Lett. 386:115-122. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. J., L. L. Decker, M. Volk, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1998. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 9:395-404. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. J., D. Hochberg, and A. D. Thorley-Lawson. 2000. The expression pattern of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity 13:497-506. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, S. 1995. Effect of genistein on in vitro and in vivo models of cancer. J. Nutr. 125:777-783. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

