Central European Dobrava Hantavirus isolate from a striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius)
- PMID: 15956394
- PMCID: PMC1151903
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2756-2763.2005
Central European Dobrava Hantavirus isolate from a striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius)
Abstract
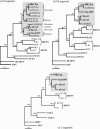
Dobrava virus (DOBV) is a hantavirus that causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Europe. It is hosted by at least two rodent species, Apodemus flavicollis and A. agrarius. According to their natural hosts they form the distinct genetic lineages DOBV-Af and DOBV-Aa, respectively. We have now established a DOBV isolate named Slovakia (SK/Aa) from an A. agrarius animal captured in Slovakia. The complete S and M and partial L segment nucleotide sequences of the new isolate were determined. Phylogenetic analyses showed that the SK/Aa isolate clustered together with the other DOBV-Aa sequences amplified from A. agrarius before and can be taken as the representative of this genetic lineage. SK/Aa, in comparison with a DOBV-Af isolate, was used for serotyping neutralizing antibodies of HFRS patients in Central Europe. Most patients' sera exhibited a higher endpoint titer when probed with our new isolate, suggesting that DOBV-Aa strains are responsible for most of the DOBV-caused HFRS cases in this region.
Figures
Comment in
-
Saaremaa hantavirus should not be confused with its dangerous relative, Dobrava virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;44(4):1608-9; author reply 1609-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.4.1608-1611.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597913 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dobrava hantavirus causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in central Europe and is carried by two different Apodemus mice species.J Med Virol. 2001 Feb;63(2):158-67. J Med Virol. 2001. PMID: 11170053
-
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by 2 lineages of Dobrava hantavirus, Russia.Emerg Infect Dis. 2008 Apr;14(4):617-25. doi: 10.3201/eid1404.071310. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18394280 Free PMC article.
-
Hantavirus disease in Germany due to infection with Dobrava-Belgrade virus genotype Kurkino.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Oct;20(10):O648-55. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12543. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24438436
-
Dobrava-Belgrade virus: phylogeny, epidemiology, disease.Antiviral Res. 2012 Aug;95(2):104-17. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 May 30. Antiviral Res. 2012. PMID: 22659378 Review.
-
Complex evolution and epidemiology of Dobrava-Belgrade hantavirus: definition of genotypes and their characteristics.Arch Virol. 2013 Mar;158(3):521-9. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1514-5. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Arch Virol. 2013. PMID: 23090188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saaremaa hantavirus should not be confused with its dangerous relative, Dobrava virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;44(4):1608-9; author reply 1609-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.4.1608-1611.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597913 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Proteinuria and the Clinical Course of Dobrava-Belgrade Hantavirus Infection.Nephron Extra. 2018 Feb 9;8(1):1-10. doi: 10.1159/000486322. eCollection 2018 Jan-Apr. Nephron Extra. 2018. PMID: 29849535 Free PMC article.
-
Sangassou virus, the first hantavirus isolate from Africa, displays genetic and functional properties distinct from those of other murinae-associated hantaviruses.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3819-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05879-11. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22278233 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Hantaviruses Harbored by Murid Rodents in Northwestern Ukraine and Discovery of a Novel Puumala Virus Strain.Viruses. 2021 Aug 18;13(8):1640. doi: 10.3390/v13081640. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452504 Free PMC article.
-
Hantaviruses induce antiviral and pro-inflammatory innate immune responses in astrocytic cells and the brain.Viral Immunol. 2014 Aug;27(6):256-66. doi: 10.1089/vim.2014.0019. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Viral Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24937036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoniadis, A., A. Stylianakis, A. Papa, S. Alexiou-Daniel, A. Lampropoulos, S. T. Nichol, C. J. Peters, and C. F. Spiropoulou. 1996. Direct genetic detection of Dobrava virus in Greek and Albanian patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 174:407-410. - PubMed
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T., K. Nemirov, M. Petrovec, T. Trilar, M. Poljak, A. Vaheri, and A. Plyusnin. 2000. Genetic analysis of wild-type Dobrava hantavirus in Slovenia: co-existence of two distinct genetic lineages within the same natural focus. J. Gen. Virol. 81:1747-1755. - PubMed
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T., M. Petrovec, P. Furlan, R. Kaps, F. Elgh, and A. Lundkvist. 1999. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in the Dolenjska region of Slovenia, a 10-year survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28:860-865. - PubMed
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T., A. Toney, K. Anderson, Y. K. Chu, and C. S. Schmaljohn. 1995. Genetic and antigenic properties of Dobrava virus: a unique member of the Hantavirus genus, family Bunyaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 76:2801-2808. - PubMed
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T., S. Y. Xiao, R. Stojanovic, A. Gligic, G. van der Groen, and J. W. LeDuc. 1992. Characterization of Dobrava virus: a hantavirus from Slovenia, Yugoslavia. J. Med. Virol. 38:132-137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

