A census of membrane-bound and intracellular signal transduction proteins in bacteria: bacterial IQ, extroverts and introverts
- PMID: 15955239
- PMCID: PMC1183210
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-5-35
A census of membrane-bound and intracellular signal transduction proteins in bacteria: bacterial IQ, extroverts and introverts
Abstract
Background: Analysis of complete microbial genomes showed that intracellular parasites and other microorganisms that inhabit stable ecological niches encode relatively primitive signaling systems, whereas environmental microorganisms typically have sophisticated systems of environmental sensing and signal transduction.
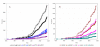
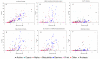
Results: This paper presents results of a comprehensive census of signal transduction proteins--histidine kinases, methyl-accepting chemotaxis receptors, Ser/Thr/Tyr protein kinases, adenylate and diguanylate cyclases and c-di-GMP phosphodiesterases--encoded in 167 bacterial and archaeal genomes, sequenced by the end of 2004. The data have been manually checked to avoid false-negative and false-positive hits that commonly arise during large-scale automated analyses and compared against other available resources. The census data show uneven distribution of most signaling proteins among bacterial and archaeal phyla. The total number of signal transduction proteins grows approximately as a square of genome size. While histidine kinases are found in representatives of all phyla and are distributed according to the power law, other signal transducers are abundant in certain phylogenetic groups but virtually absent in others.
Conclusion: The complexity of signaling systems differs even among closely related organisms. Still, it usually can be correlated with the phylogenetic position of the organism, its lifestyle, and typical environmental challenges it encounters. The number of encoded signal transducers (or their fraction in the total protein set) can be used as a measure of the organism's ability to adapt to diverse conditions, the 'bacterial IQ', while the ratio of transmembrane receptors to intracellular sensors can be used to define whether the organism is an 'extrovert', actively sensing the environmental parameters, or an 'introvert', more concerned about its internal homeostasis. Some of the microorganisms with the highest IQ, including the current leader Wolinella succinogenes, are found among the poorly studied beta-, delta- and epsilon-proteobacteria. Among all bacterial phyla, only cyanobacteria appear to be true introverts, probably due to their capacity to conduct oxygenic photosynthesis, using a complex system of intracellular membranes. The census data, available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Complete_Genomes/SignalCensus.html, can be used to get an insight into metabolic and behavioral propensities of each given organism and improve prediction of the organism's properties based solely on its genome sequence.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phyletic Distribution and Lineage-Specific Domain Architectures of Archaeal Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 12;200(7):e00681-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00681-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29263101 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of heritage and habitat in the distribution of bacterial signal transduction systems.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Apr;6(4):721-8. doi: 10.1039/b908047c. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20237650 Free PMC article.
-
Sentra: a database of signal transduction proteins for comparative genome analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D271-3. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl949. Epub 2006 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17135204 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sensory and signal-transducing domains in two-component signaling systems.Methods Enzymol. 2007;422:47-74. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)22003-2. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17628134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What bacteria want.Environ Microbiol. 2018 Dec;20(12):4221-4229. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14398. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30187651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complex Interplay between FleQ, Cyclic Diguanylate and Multiple σ Factors Coordinately Regulates Flagellar Motility and Biofilm Development in Pseudomonas putida.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 16;11(9):e0163142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163142. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27636892 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of wolbachia genomes reveals streamlining and divergence of minimalist two-component systems.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Mar 24;5(5):983-96. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.017137. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 25809075 Free PMC article.
-
Sensor complexes regulating two-component signal transduction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007 Dec;17(6):706-15. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.08.019. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007. PMID: 17913492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of sensor kinases in the stress tolerance response of Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jan;190(1):68-77. doi: 10.1128/JB.00990-07. Epub 2007 Oct 26. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 17965153 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of two-component regulatory proteins in Pseudomonas syringae.BMC Genomics. 2007 Oct 31;8:397. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-397. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17971244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sondej M, Weinglass AB, Peterkofsky A, Kaback HR. Binding of enzyme IIAGlc, a component of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system, to the Escherichia coli lactose permease. Biochemistry. 2002;41:5556–5565. - PubMed
-
- Galperin MY, Nikolskaya AN, Koonin EV. Novel domains of the prokaryotic two-component signal transduction systems. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001;203:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Mizuno T, Kaneko T, Tabata S. Compilation of all genes encoding bacterial two-component signal transducers in the genome of the cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. DNA Res. 1996;3:407–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

