The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits
- PMID: 15951850
- PMCID: PMC1142213
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.1.51
The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits
Abstract
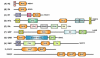
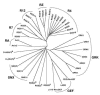
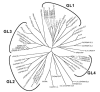
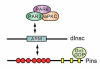
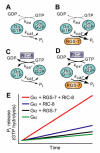
The heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunit has long been considered a bimodal, GTP-hydrolyzing switch controlling the duration of signal transduction by seven-transmembrane domain (7TM) cell-surface receptors. In 1996, we and others identified a superfamily of "regulator of G-protein signaling" (RGS) proteins that accelerate the rate of GTP hydrolysis by Galpha subunits (dubbed GTPase-accelerating protein or "GAP" activity). This discovery resolved the paradox between the rapid physiological timing seen for 7TM receptor signal transduction in vivo and the slow rates of GTP hydrolysis exhibited by purified Galpha subunits in vitro. Here, we review more recent discoveries that have highlighted newly-appreciated roles for RGS proteins beyond mere negative regulators of 7TM signaling. These new roles include the RGS-box-containing, RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RGS-RhoGEFs) that serve as Galpha effectors to couple 7TM and semaphorin receptor signaling to RhoA activation, the potential for RGS12 to serve as a nexus for signaling from tyrosine kinases and G-proteins of both the Galpha and Ras-superfamilies, the potential for R7-subfamily RGS proteins to couple Galpha subunits to 7TM receptors in the absence of conventional Gbetagamma dimers, and the potential for the conjoint 7TM/RGS-box Arabidopsis protein AtRGS1 to serve as a ligand-operated GAP for the plant Galpha AtGPA1. Moreover, we review the discovery of novel biochemical activities that also impinge on the guanine nucleotide binding and hydrolysis cycle of Galpha subunits: namely, the guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) activity of the GoLoco motif-containing proteins and the 7TM receptor-independent guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity of Ric8/synembryn. Discovery of these novel GAP, GDI, and GEF activities have helped to illuminate a new role for Galpha subunit GDP/GTP cycling required for microtubule force generation and mitotic spindle function in chromosomal segregation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

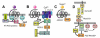

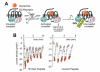

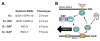
Similar articles
-
G protein activation without a GEF in the plant kingdom.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jun;8(6):e1002756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002756. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22761582 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(12):4053-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4053-4061.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12024019 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G-protein signalling and GoLoco proteins suppress TRPC4 channel function via acting at Gαi/o.Biochem J. 2016 May 15;473(10):1379-90. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160214. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26987813 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence-based assays for RGS box function.Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:56-71. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89004-9. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 15313559 Review.
-
Regulators of G-protein signaling and their Gα substrates: promises and challenges in their use as drug discovery targets.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Sep;63(3):728-49. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003038. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21737532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-188-5p promotes oxaliplatin resistance by targeting RASA1 in colon cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jun;21(6):481. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12742. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33968197 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RGS5 GAP activity by GPSM3.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Jul;405(1-2):33-40. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2393-3. Epub 2015 Apr 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25842189
-
Hypoxic induction of the regulator of G-protein signalling 4 gene is mediated by the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044564. Epub 2012 Sep 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970249 Free PMC article.
-
Class VI G protein-coupled receptors in Aspergillus oryzae regulate sclerotia formation through GTPase-activating activity.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 17;108(1):141. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12862-0. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38231240 Free PMC article.
-
The RGS protein inhibitor CCG-4986 is a covalent modifier of the RGS4 Galpha-interaction face.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Sep;1774(9):1213-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17660054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilman AG. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–49. - PubMed
-
- Hamm HE. The many faces of G protein signaling. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(2):669–72. - PubMed
-
- Offermanns S. G-proteins as transducers in transmembrane signalling. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003;83(2):101–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

