Selective Runx2-II deficiency leads to low-turnover osteopenia in adult mice
- PMID: 15936013
- PMCID: PMC1360182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.04.028
Selective Runx2-II deficiency leads to low-turnover osteopenia in adult mice
Abstract
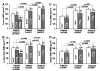
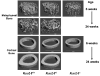
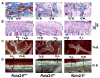
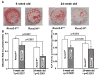
Runx2 transcribes Runx2-II and Runx2-I isoforms with distinct N-termini. Deletion of both isoforms results in complete arrest of bone development, whereas selective loss of Runx2-II is sufficient to form a grossly intact skeleton with impaired endochondral bone development. To elucidate the role of Runx2-II in osteoblast function in adult mice, we examined heterozygous Runx2-II (Runx2-II(+/-)) and homozygous Runx2-II (Runx2-II(-/-))-deficient mice, which, respectively, lack one or both copies of Runx2-II but intact Runx2-I expression. Compared to wild-type mice, 6-week-old Runx2-II(+/-) had reduced trabecular bone volume (BV/TV%), cortical thickness (Ct.Th), and bone mineral density (BMD), decreased osteoblastic and osteoclastic markers, lower bone formation rates, impaired osteoblast maturation of BMSCs in vitro, and significant reductions in mechanical properties. Homozygous Runx2-II(-/-) mice had a more severe reduction in BMD, BV/TV%, and Ct.Th, and greater suppression of osteoblastic and osteoclastic markers than Runx2-II(+/-) mice. Non-selective Runx2(+/-) mice, which have an equivalent reduction in Runx2 expression due to the lack one copy of Runx2-I and II, however, had an intermediate reduction in BMD. Thus, selective Runx2-II mutation causes diminished osteoblastic function in an adult mouse leading to low-turnover osteopenia and suggest that Runx2-I and II have distinct functions imparted by their different N-termini.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aged mice require full transcription factor, Runx2/Cbfa1, gene dosage for cancellous bone regeneration after bone marrow ablation.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Sep;19(9):1481-9. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040601. Epub 2004 Jun 7. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15312248
-
High bone resorption in adult aging transgenic mice overexpressing cbfa1/runx2 in cells of the osteoblastic lineage.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;22(17):6222-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.17.6222-6233.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12167715 Free PMC article.
-
Selective deficiency of the "bone-related" Runx2-II unexpectedly preserves osteoblast-mediated skeletogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):20307-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401109200. Epub 2004 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15007057
-
Fhl2 deficiency results in osteopenia due to decreased activity of osteoblasts.EMBO J. 2005 Sep 7;24(17):3049-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600773. Epub 2005 Aug 4. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 16079911 Free PMC article.
-
Control of postnatal bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1116:174-81. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.044. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18083927 Review.
Cited by
-
Fermented Oyster Extract Promotes Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1-Mediated Osteogenesis and Growth Rate.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 18;18(9):472. doi: 10.3390/md18090472. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32962034 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of Runx1 transcription factor impairs the development of thymocytes from the double-negative to double-positive stages.Immunology. 2010 Jun;130(2):243-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03230.x. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20102410 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Mecom in mouse results in early-onset spinal deformity and osteopenia.Bone. 2014 Mar;60:148-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.11.020. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24316420 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin VII regulates bone remodeling by modulating osteoclast and osteoblast secretion.Dev Cell. 2008 Jun;14(6):914-25. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.03.022. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18539119 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Kif3a in osteoblasts results in defective bone formation and osteopenia.J Cell Sci. 2012 Apr 15;125(Pt 8):1945-57. doi: 10.1242/jcs.095893. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22357948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee C, Javed A, Choi JY, Green J, Rosen V, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB, Stein GS. Differential regulation of the two principal Runx2/Cbfa1 N-terminal isoforms in response to bone morphogenetic protein-2 during development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrinology. 2001;142:4026–4039. - PubMed
-
- Choi JY, Pratap J, Javed A, Zaidi SK, Xing L, Balint E, Dalamangas S, Boyce B, van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Stein JL, Jones SN, Stein GS. Subnuclear targeting of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors is essential for tissue-specific differentiation during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:8650–8655. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi KY, Lee SW, Park MH, Bae YC, Shin HI, Nam S, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Ryoo HM. Spatio-temporal expression patterns of Runx2 isoforms in early skeletogenesis. Exp Mol Med. 2002;34:426–433. - PubMed
-
- Chung UI, Kawaguchi H, Takato T, Nakamura K. Distinct osteogenic mechanisms of bones of distinct origins. J Orthop Sci. 2004;9:410–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

