In vitro antiviral activity and single-dose pharmacokinetics in humans of a novel, orally bioavailable inhibitor of human rhinovirus 3C protease
- PMID: 15917520
- PMCID: PMC1140523
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.6.2267-2275.2005
In vitro antiviral activity and single-dose pharmacokinetics in humans of a novel, orally bioavailable inhibitor of human rhinovirus 3C protease
Abstract
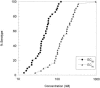
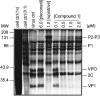
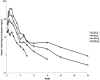
(E)-(S)-4-((S)-2-{3-[(5-methyl-isoxazole-3-carbonyl)-amino]-2-oxo-2H-pyridin-1-yl}-pent-4-ynoylamino)-5-((S)-2-oxo-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-pent-2-enoic acid ethyl ester (Compound 1) is a novel, irreversible inhibitor of human rhinovirus (HRV) 3C protease {inactivation rate constant (Kobs/[I]) of 223,000 M-1s-1}. In cell-based assays, Compound 1 was active against all HRV serotypes (35 of 35), HRV clinical isolates (5 of 5), and related picornaviruses (8 of 8) tested with mean 50% effective concentration (EC50) values of 50 nM (range, 14 to 122 nM), 77 nM (range, 72 to 89 nM), and 75 nM (range, 7 to 249 nM), respectively. Compound 1 inhibited HRV 3C-mediated polyprotein processing in infected cells in a concentration-dependent manner, providing direct confirmation that the cell-based antiviral activity is due to inhibition of 3C protease. In vitro and in vivo nonclinical safety studies showed Compound 1 to be without adverse effects at maximum achievable doses. Single oral doses of Compound 1 up to 2,000 mg in healthy volunteers were found to be safe and well tolerated in a phase I-ascending, single-dose study. Compound 1 estimated free observed maximum concentration in plasma (Cmax) for 500-, 1,000-, and 2,000-mg doses were higher than the protein binding-corrected EC50 required to inhibit 80% of the HRV serotypes tested. Treatment of HRV 52-infected cells with one to five 2-h pulses of 150 nM Compound 1 (corresponding to the Cmax at the 500-mg dose) was sufficient to effect a significant reduction in viral replication. These experiments highlight Compound 1 as a potent, orally bioavailable, irreversible inhibitor of HRV 3C protease and provide data that suggest that Cmax rather than the Cmin might be the key variable predicting clinical efficacy.
Figures
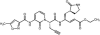
Similar articles
-
Conservation of amino acids in human rhinovirus 3C protease correlates with broad-spectrum antiviral activity of rupintrivir, a novel human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitor.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Feb;49(2):619-26. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.619-626.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15673742 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of irreversible human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitors. 8. Pharmacological optimization of orally bioavailable 2-pyridone-containing peptidomimetics.J Med Chem. 2003 Oct 9;46(21):4572-85. doi: 10.1021/jm030166l. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14521419
-
Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of irreversible human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitors. 2. Peptide structure-activity studies.J Med Chem. 1998 Jul 16;41(15):2819-34. doi: 10.1021/jm9800696. J Med Chem. 1998. PMID: 9667971
-
Human rhinovirus 3C protease as a potential target for the development of antiviral agents.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007 Feb;8(1):19-27. doi: 10.2174/138920307779941523. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007. PMID: 17305557 Review.
-
Proteases of human rhinovirus: role in infection.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1221:129-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1571-2_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25261311 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and inhibition of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 main proteases by oral antiviral compound AG7404.Antiviral Res. 2022 Dec;208:105458. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105458. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Antiviral Res. 2022. PMID: 36336176 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Substrate Envelope of Enterovirus 68-3C Protease: Structural Basis of Specificity and Potential Resistance.Viruses. 2024 Sep 5;16(9):1419. doi: 10.3390/v16091419. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339895 Free PMC article.
-
Rupintrivir is a promising candidate for treating severe cases of Enterovirus-71 infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Jan 14;16(2):201-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i2.201. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20066739 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory virus modulation of host nucleocytoplasmic transport; target for therapeutic intervention?Front Microbiol. 2015 Aug 14;6:848. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00848. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26322040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations for the discovery and development of 3-chymotrypsin-like cysteine protease inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 infection.Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Aug;49:36-40. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.04.006. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34029993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arruda, E., and F. G. Hayden. 1995. Clinical studies of antiviral agents for picornaviral infections, p. 321-355, In D. J. Jeffries and E. De Clerq (ed.), Antiviral chemotherapy. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, United Kingdom.
-
- Atmar, R. L., E. Guy, K. K. Guntupalli, J. L. Zimmerman, V. D. Bandi, B. D. Baxter, and S. B. Greenberg. 1998. Respiratory tract viral infections in inner-city asthmatic adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 158:2453-2459. - PubMed
-
- Binford, S. L., F. Maldonado, M. A. Brothers, P. T. Weady, L. S. Zalman, J. W. Meador III, D. A. Matthews, and A. K. Patick. Conservation of amino acids in human rhinovirus 3C protease correlates with broad spectrum antiviral activity of rupintrivir, a novel human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., in press. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brun, S., D. Kempf, K. Garren, A. Molla, M. King, B. Richards, T. Marsh, R. Bertz, A. Hsu, and E. Sun. 2001. The inhibitory quotient as a predictor of viral evolution following viral load rebound during Lopinavir/r therapy, poster no. 89. 5th International Workshop on HIV Drug Resistance and Treatment Strategies, Scottsdale, Ariz.
-
- Cheah, K.-C., L. E.-C. Leong, and A. G. Porter. 1990. Site-directed mutagenesis suggests close functional relationship between a human rhinovirus 3C cysteine protease and cellular trypsin-like serine proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 265:7180-7187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

