Genetic and cell biological characterization of the vaccinia virus A30 and G7 phosphoproteins
- PMID: 15890954
- PMCID: PMC1112092
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.7146-7161.2005
Genetic and cell biological characterization of the vaccinia virus A30 and G7 phosphoproteins
Abstract
The vaccinia virus proteins A30 and G7 are known to play essential roles in early morphogenesis, acting prior to the formation of immature virions. Their repression or inactivation results in the accumulation of large virosomes, detached membrane crescents, and empty immature virions. We have undertaken further study of these proteins to place them within the context of the F10 kinase, the A14 membrane protein, and the H5 phosphoprotein, which have been the focus of previous studies within our laboratory. Here we confirm that both A30 and G7 undergo F10 kinase-dependent phosphorylation in vivo and recapitulate that modification of A30 in vitro. Although the detached crescents observed upon loss of A30 or G7 echo those seen upon repression of A14, no interaction between A30/G7 and A14 could be detected. We did, however, determine that the A30 and G7 proteins are unstable during nonpermissive tsH5 infections, suggesting that the loss of A30/G7 is the underlying cause for the formation of lacy or curdled virosomes. We also determined that the temperature-sensitive phenotype of the Cts11 virus is due to mutations in two codons of the G7L gene. Phenotypic analysis of nonpermissive Cts11 infections indicated that these amino acid substitutions compromise G7 function without impairing the stability of either G7 or A30. Utilizing Cts11 in conjunction with a rifampin release assay, we determined that G7 acts at multiple stages of virion morphogenesis that can be distinguished both by ultrastructural analysis and by monitoring the phosphorylation status of several viral proteins that undergo F10-mediated phosphorylation.
Figures
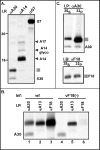
 ), and the α-A14 precipitate contained the ∼21-kDa A17 protein, as well as A14 and a small amount of glycosylated A14 (A14 glyco). No interaction between A30 and G7 was detected. The precipitated proteins are identified at the right; molecular markers are shown at the left, with their masses given in kilodaltons. (B) The 11-kDa protein coprecipitating with A30 migrates with A13 and F18 and is not retrieved when F18 expression is repressed. Cells were infected with either wt virus (lanes 1 to 3) or the inducible F18 recombinant in the absence of IPTG (vF18[−], lanes 4 to 6). Cells were metabolically labeled and subjected to immunoprecipitation as described for panel A. (C) The 11-kDa protein that coprecipitates with A30 is the viral F18 protein. Cells infected with wt virus (as described in panel A) were pulse-labeled with either [35S]methionine or [32P]Pi and subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-A30. The immunoprecipitates were resolved in duplicate by SDS-PAGE; one set was visualized directly by autoradiography (I.P.; top), and the second was subjected to immunoblot analysis with α-F18 serum (I.B.; bottom).
), and the α-A14 precipitate contained the ∼21-kDa A17 protein, as well as A14 and a small amount of glycosylated A14 (A14 glyco). No interaction between A30 and G7 was detected. The precipitated proteins are identified at the right; molecular markers are shown at the left, with their masses given in kilodaltons. (B) The 11-kDa protein coprecipitating with A30 migrates with A13 and F18 and is not retrieved when F18 expression is repressed. Cells were infected with either wt virus (lanes 1 to 3) or the inducible F18 recombinant in the absence of IPTG (vF18[−], lanes 4 to 6). Cells were metabolically labeled and subjected to immunoprecipitation as described for panel A. (C) The 11-kDa protein that coprecipitates with A30 is the viral F18 protein. Cells infected with wt virus (as described in panel A) were pulse-labeled with either [35S]methionine or [32P]Pi and subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-A30. The immunoprecipitates were resolved in duplicate by SDS-PAGE; one set was visualized directly by autoradiography (I.P.; top), and the second was subjected to immunoblot analysis with α-F18 serum (I.B.; bottom).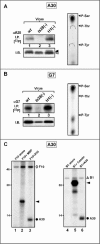



Similar articles
-
Physical and functional interactions between vaccinia virus F10 protein kinase and virion assembly proteins A30 and G7.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(1):266-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.1.266-274.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14671108 Free PMC article.
-
A complex of seven vaccinia virus proteins conserved in all chordopoxviruses is required for the association of membranes and viroplasm to form immature virions.Virology. 2004 Dec 20;330(2):447-59. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.10.008. Virology. 2004. PMID: 15567438
-
Vaccinia virus mutants with alanine substitutions in the conserved G5R gene fail to initiate morphogenesis at the nonpermissive temperature.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(19):10238-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.19.10238-10248.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15367589 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus morphogenesis: a13 phosphoprotein is required for assembly of mature virions.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(16):8885-901. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8885-8901.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15280497 Free PMC article.
-
In a nutshell: structure and assembly of the vaccinia virion.Adv Virus Res. 2006;66:31-124. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66002-8. Adv Virus Res. 2006. PMID: 16877059 Review.
Cited by
-
Poxvirus proteomics and virus-host protein interactions.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Dec;73(4):730-49. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00026-09. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19946139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral serine/threonine protein kinases.J Virol. 2011 Feb;85(3):1158-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01369-10. Epub 2010 Nov 17. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21084474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and Characterization of vΔI3 Confirm that Vaccinia Virus SSB Plays an Essential Role in Viral Replication.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e01719-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01719-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29093092 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus mutations in the L4R gene encoding a virion structural protein produce abnormal mature particles lacking a nucleocapsid.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14017-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02126-14. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25253347 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus protein A3 is required for the production of normal immature virions and for the encapsidation of the nucleocapsid protein L4.Virology. 2015 Jul;481:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25765002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banham, A. H., and G. L. Smith. 1992. Vaccinia virus gene B1R encodes a 34-kDa serine/threonine protein kinase that localizes in cytoplasmic factories and is packaged into virions. Virology 191:803-812. - PubMed
-
- Black, E. P., N. Moussatche, and R. C. Condit. 1998. Characterization of the interactions among vaccinia virus transcription factors G2R, A18R, and H5R. Virology 245:313-322. - PubMed
-
- Dales, S., and E. H. Mosbach. 1968. Vaccinia as a model for membrane biogenesis. Virology 35:564-583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

