RMI1/NCE4, a suppressor of genome instability, encodes a member of the RecQ helicase/Topo III complex
- PMID: 15889139
- PMCID: PMC1142613
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600684
RMI1/NCE4, a suppressor of genome instability, encodes a member of the RecQ helicase/Topo III complex
Abstract
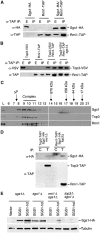
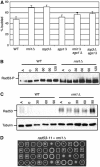
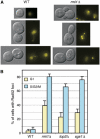
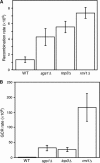
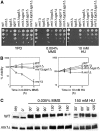
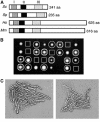
SGS1 encodes a DNA helicase whose homologues in human cells include the BLM, WRN, and RECQ4 genes, mutations in which lead to cancer-predisposition syndromes. Clustering of synthetic genetic interactions identified by large-scale genetic network analysis revealed that the genetic interaction profile of the gene RMI1 (RecQ-mediated genome instability, also known as NCE4 and YPL024W) was highly similar to that of SGS1 and TOP3, suggesting a functional relationship between Rmi1 and the Sgs1/Top3 complex. We show that Rmi1 physically interacts with Sgs1 and Top3 and is a third member of this complex. Cells lacking RMI1 activate the Rad53 checkpoint kinase, undergo a mitotic delay, and display increased relocalization of the recombination repair protein Rad52, indicating the presence of spontaneous DNA damage. Consistent with a role for RMI1 in maintaining genome integrity, rmi1Delta cells exhibit increased recombination frequency and increased frequency of gross chromosomal rearrangements. In addition, rmi1Delta strains fail to fully activate Rad53 upon exposure to DNA-damaging agents, suggesting that Rmi1 is also an important part of the Rad53-dependent DNA damage response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yeast Rmi1/Nce4 controls genome stability as a subunit of the Sgs1-Top3 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;25(11):4476-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.11.4476-4487.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15899853 Free PMC article.
-
SGS1, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue of BLM and WRN, suppresses genome instability and homeologous recombination.Nat Genet. 2001 Jan;27(1):113-6. doi: 10.1038/83673. Nat Genet. 2001. PMID: 11138010
-
[Functional analysis of yeast homologue gene associated with human DNA helicase causative syndromes].Kokuritsu Iyakuhin Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyusho Hokoku. 2002;(120):53-74. Kokuritsu Iyakuhin Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyusho Hokoku. 2002. PMID: 12638184 Review. Japanese.
-
Binding and activation of DNA topoisomerase III by the Rmi1 subunit.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28971-28979. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705427200. Epub 2007 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17693398 Free PMC article.
-
Smc5/6 complex regulates Sgs1 recombination functions.Curr Genet. 2017 Jun;63(3):381-388. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0648-5. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27664093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
All tangled up: how cells direct, manage and exploit topoisomerase function.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Nov 23;12(12):827-41. doi: 10.1038/nrm3228. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22108601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RMI1 promotes DNA replication fork progression and recovery from replication fork stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;32(15):3054-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00255-12. Epub 2012 May 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22645306 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory control of Sgs1 and Dna2 during eukaryotic DNA end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 26;116(13):6091-6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819276116. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30850524 Free PMC article.
-
Epistasis analysis between homologous recombination genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identifies multiple repair pathways for Sgs1, Mus81-Mms4 and RNase H2.Mutat Res. 2011 Sep 1;714(1-2):33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Mutat Res. 2011. PMID: 21741981 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase 3alpha and RMI1 suppress somatic crossovers and are essential for resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS Genet. 2008 Dec;4(12):e1000285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000285. Epub 2008 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 19096507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajima J, Umezu K, Maki H (2002) Elevated incidence of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in an sgs1 mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: roles of yeast RecQ helicase in suppression of aneuploidy, interchromosomal rearrangement, and the simultaneous incidence of both events during mitotic growth. Mutat Res 504: 157–172 - PubMed
-
- Bennett RJ, Noirot-Gros MF, Wang JC (2000) Interaction between yeast sgs1 helicase and DNA topoisomerase III. J Biol Chem 275: 26898–26905 - PubMed
-
- Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD (1998) Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14: 115–132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

