ELKS, a protein structurally related to the active zone-associated protein CAST, is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and functions in insulin exocytosis: interaction of ELKS with exocytotic machinery analyzed by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
- PMID: 15888548
- PMCID: PMC1165411
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0816
ELKS, a protein structurally related to the active zone-associated protein CAST, is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and functions in insulin exocytosis: interaction of ELKS with exocytotic machinery analyzed by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
Abstract
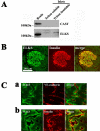
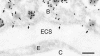
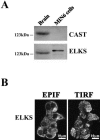
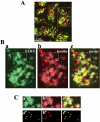
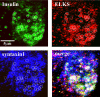
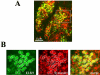
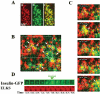
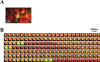
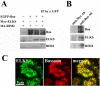
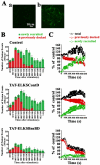
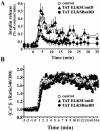
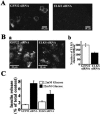
The cytomatrix at the active zone (CAZ) has been implicated in defining the site of Ca2+-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitters. Here, we demonstrate the expression and function of ELKS, a protein structurally related to the CAZ protein CAST, in insulin exocytosis. The results of confocal and immunoelectron microscopic analysis showed that ELKS is present in pancreatic beta cells and is localized close to insulin granules docked on the plasma membrane-facing blood vessels. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy imaging in insulin-producing clonal cells revealed that the ELKS clusters are less dense and unevenly distributed than syntaxin 1 clusters, which are enriched in the plasma membrane. Most of the ELKS clusters were on the docking sites of insulin granules that were colocalized with syntaxin 1 clusters. Total internal reflection fluorescence images of single-granule motion showed that the fusion events of insulin granules mostly occurred on the ELKS cluster, where repeated fusion was sometimes observed. When the Bassoon-binding region of ELKS was introduced into the cells, the docking and fusion of insulin granules were markedly reduced. Moreover, attenuation of ELKS expression by small interfering RNA reduced the glucose-evoked insulin release. These data suggest that the CAZ-related protein ELKS functions in insulin exocytosis from pancreatic beta cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Site of docking and fusion of insulin secretory granules in live MIN6 beta cells analyzed by TAT-conjugated anti-syntaxin 1 antibody and total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):8403-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308954200. Epub 2003 Dec 15. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14676208
-
ELKS/Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channel-β Subunit Module Regulates Polarized Ca2+ Influx in Pancreatic β Cells.Cell Rep. 2019 Jan 29;26(5):1213-1226.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.106. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30699350
-
Role of the active zone protein, ELKS, in insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells.Mol Metab. 2019 Sep;27S(Suppl):S81-S91. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.06.017. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31500835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exophilin8 transiently clusters insulin granules at the actin-rich cell cortex prior to exocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 May 15;22(10):1716-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-05-0404. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21441305 Free PMC article.
-
ELKS active zone proteins as multitasking scaffolds for secretion.Open Biol. 2018 Feb;8(2):170258. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170258. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 29491150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The changing view of insulin granule mobility: From conveyor belt to signaling hub.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 2;13:983152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.983152. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36120467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic Active Zone Density during Development and Synaptic Plasticity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Feb 15;5:12. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00012. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22438837 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubules regulate pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity via spatiotemporal control of insulin secretion hot spots.Elife. 2021 Nov 16;10:e59912. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59912. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34783306 Free PMC article.
-
12p13.33 microdeletion including ELKS/ERC1, a new locus associated with childhood apraxia of speech.Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Jan;21(1):82-8. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.116. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 22713806 Free PMC article.
-
Routing of the RAB6 secretory pathway towards the lysosome related organelle of melanocytes.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 13;8:15835. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15835. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28607494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akimoto, Y., Kreppel, L. K., Hirano, H., and Hart, G. W. (1999). Localization of the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase in rat pancreas. Diabetes 48, 2407–2413. - PubMed
-
- Altrock, W. D., et al. (2003). Functional inactivation of a fraction of excitatory synapses in mice deficient for the active zone protein bassoon. Neuron 37, 787–800. - PubMed
-
- Betz, A., Thakur, P., Junge, H. J., Ashery, U., Rhee, J. S., Scheuss, V., Rosenmund, C., Rettig, J., and Brose, N. (2001). Functional interaction of the active zone proteins Munc13–1 and RIM1 in synaptic vesicle priming. Neuron 30, 183–196. - PubMed
-
- Brose, N., Rosenmond, C., and Rettig, J. (2000). Regulation of transmitter release by Unc-13 and its homologues. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 303–311. - PubMed
-
- Burns, M. E., and Augustine., G. J. (1995). Synaptic structure and function: dynamic organization yields architectural precision. Cell 83, 187–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

