A novel RNA-binding protein in neuronal RNA granules: regulatory machinery for local translation
- PMID: 15858068
- PMCID: PMC6725113
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0382-05.2005
A novel RNA-binding protein in neuronal RNA granules: regulatory machinery for local translation
Abstract
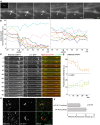
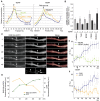
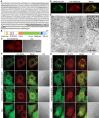
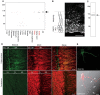
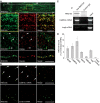
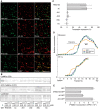
Local translation in neuronal dendrites is an important basis for long-term synaptic plasticity, and RNA granules in the dendrites are involved in the local translation. Here, we identify RNG105 (RNA granule protein 105), a novel RNA-binding protein, as a component of the RNA granules in dendrites of hippocampal neurons. The RNG105-localizing RNA granules contain mRNAs, the translational products of which play key roles in synaptic plasticity. RNG105 has an ability to repress translation both in vitro and in vivo, consistent with the finding that the RNA granule is translationally arrested in the basal conditions. Dissociation of RNG105 from the RNA granules is induced by BDNF, a growth factor responsible for synaptic plasticity. The RNG105 dissociation is coincident with the induction of local translation near the granules. These findings suggest that RNG105 is a translational repressor in the RNA granules and provide insight into the link between RNG105 dynamics and local translational regulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA granule protein 140 (RNG140), a paralog of RNG105 localized to distinct RNA granules in neuronal dendrites in the adult vertebrate brain.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 30;285(31):24260-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.108944. Epub 2010 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20516077 Free PMC article.
-
Cataloguing and Selection of mRNAs Localized to Dendrites in Neurons and Regulated by RNA-Binding Proteins in RNA Granules.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 22;10(2):167. doi: 10.3390/biom10020167. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31978946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic localization of the translational repressor Pumilio 2 and its contribution to dendritic stress granules.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 14;26(24):6496-508. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0649-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16775137 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43, the signature protein of FTLD-U, is a neuronal activity-responsive factor.J Neurochem. 2008 May;105(3):797-806. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05190.x. Epub 2007 Dec 15. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18088371
-
Analysis of mRNA translation in cultured hippocampal neurons.Methods Enzymol. 2007;431:143-62. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)31008-2. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17923234 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA transport and local control of translation.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:223-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.122303.120653. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16212494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CPEB3 low-complexity motif regulates local protein synthesis via protein-protein interactions in neuronal ribonucleoprotein granules.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Feb 7;120(6):e2114747120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2114747120. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36716374 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and genetic analysis of the Drosophila model of fragile X syndrome.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012;54:119-56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21649-7_7. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012. PMID: 22009350 Free PMC article.
-
Stress granule subtypes: an emerging link to neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Dec;77(23):4827-4845. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03565-0. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32500266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing the functional utility of PAR-CLIP by quantifying background binding to mRNAs and lncRNAs.Genome Biol. 2014 Jan 7;15(1):R2. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r2. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24393468 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

