Central ions and lateral asparagine/glutamine zippers stabilize the post-fusion hairpin conformation of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein
- PMID: 15840526
- PMCID: PMC7111771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.02.022
Central ions and lateral asparagine/glutamine zippers stabilize the post-fusion hairpin conformation of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein
Abstract
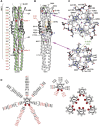
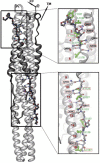
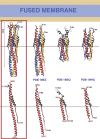
The coronavirus spike glycoprotein is a class I membrane fusion protein with two characteristic heptad repeat regions (HR1 and HR2) in its ectodomain. Here, we report the X-ray structure of a previously characterized HR1/HR2 complex of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. As expected, the HR1 and HR2 segments are organized in antiparallel orientations within a rod-like molecule. The HR1 helices form an exceptionally long (120 A) internal coiled coil stabilized by hydrophobic and polar interactions. A striking arrangement of conserved asparagine and glutamine residues of HR1 propagates from two central chloride ions, providing hydrogen-bonding "zippers" that strongly constrain the path of the HR2 main chain, forcing it to adopt an extended conformation at either end of a short HR2 alpha-helix.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between heptad repeat 1 and 2 regions in spike protein of SARS-associated coronavirus: implications for virus fusogenic mechanism and identification of fusion inhibitors.Lancet. 2004 Mar 20;363(9413):938-47. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15788-7. Lancet. 2004. PMID: 15043961 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus heptad repeat 2 domain in the prefusion state.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 28;281(17):11965-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601174200. Epub 2006 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16507566 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection inhibition using spike protein heptad repeat-derived peptides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 1;101(22):8455-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400576101. Epub 2004 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15150417 Free PMC article.
-
Multimerization of the heptad repeat regions of the SARS-CoV 2 spike protein.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2024 Feb;1866(2):184259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2023.184259. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2024. PMID: 38061554 Review.
-
The SARS-CoV S glycoprotein.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Oct;61(19-20):2428-30. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4257-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15526150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico anti-viral assessment of phytoconstituents in a traditional (Siddha Medicine) polyherbal formulation - Targeting Mpro and pan-coronavirus post-fusion Spike protein.J Tradit Complement Med. 2023 Jul 13;14(1):55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.07.004. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Tradit Complement Med. 2023. PMID: 38223813 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid acyl chain protrusion induced by the influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide detected by NMR paramagnetic relaxation enhancement.Biophys Chem. 2023 Aug;299:107028. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2023.107028. Epub 2023 May 13. Biophys Chem. 2023. PMID: 37247572 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Stabilization Strategies.Viruses. 2023 Feb 17;15(2):558. doi: 10.3390/v15020558. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Epitope Candidates for SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2022 Aug 21;14(8):1837. doi: 10.3390/v14081837. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016459 Free PMC article.
-
Structural polymorphism of coiled-coils from the stalk domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.FASEB J. 2022 Mar;36(3):e22199. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101670R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35157347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akey D.L., Malashkevich V.N., Kim P.S. Buried polar residues in coiled-coil interfaces. Biochemistry. 2001;40(21):6352–6360. - PubMed
-
- Baker K.A., Dutch R.E., Lamb R.A., Jardetzky T.S. Structural basis for paramyxovirus-mediated membrane fusion. Mol. Cell. 1999;3(3):309–319. - PubMed
-
- Bosch B.J., Martina B.E., Van Der Zee R., Lepault J., Haijema B.J., Versluis C., Heck A.J., De Groot R., Osterhaus A.D., Rottier P.J. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection inhibition using spike protein heptad repeat-derived peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004;101(22):8455–8460. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

