tRNA m7G methyltransferase Trm8p/Trm82p: evidence linking activity to a growth phenotype and implicating Trm82p in maintaining levels of active Trm8p
- PMID: 15811913
- PMCID: PMC1370766
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2030705
tRNA m7G methyltransferase Trm8p/Trm82p: evidence linking activity to a growth phenotype and implicating Trm82p in maintaining levels of active Trm8p
Abstract
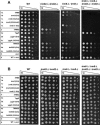
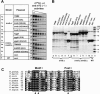
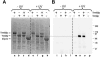
We show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains lacking Trm8p/Trm82p tRNA m7G methyltransferase are temperature-sensitive in synthetic media containing glycerol. Bacterial TRM8 orthologs complement the growth defect of trm8-Delta, trm82-Delta, and trm8-Delta trm82-Delta double mutants, suggesting that bacteria employ a single subunit for Trm8p/Trm82p function. The growth phenotype of trm8 mutants correlates with lack of tRNA m7G methyltransferase activity in vitro and in vivo, based on analysis of 10 mutant alleles of trm8 and bacterial orthologs, and suggests that m7G modification is the cellular function important for growth. Initial examination of the roles of the yeast subunits shows that Trm8p has most of the functions required to effect m7G modification, and that a major role of Trm82p is to maintain cellular levels of Trm8p. Trm8p efficiently cross-links to pre-tRNAPhe in vitro in the presence or absence of Trm82p, in addition to its known residual tRNA m7G modification activity and its SAM-binding domain. Surprisingly, the levels of Trm8p, but not its mRNA, are severely reduced in a trm82-Delta strain. Although Trm8p can be produced in the absence of Trm82p by deliberate overproduction, the resulting protein is inactive, suggesting that a second role of Trm82p is to stabilize Trm8p in an active conformation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Two proteins that form a complex are required for 7-methylguanosine modification of yeast tRNA.RNA. 2002 Oct;8(10):1253-66. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202024019. RNA. 2002. PMID: 12403464 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid tRNA decay can result from lack of nonessential modifications.Mol Cell. 2006 Jan 6;21(1):87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.036. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16387656
-
Hetero subunit interaction and RNA recognition of yeast tRNA (m7G46) methyltransferase synthesized in a wheat germ cell-free translation system.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007;(51):359-60. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrm180. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007. PMID: 18029735
-
Two-subunit enzymes involved in eukaryotic post-transcriptional tRNA modification.RNA Biol. 2014;11(12):1608-18. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1008360. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 25625329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transfer RNA methytransferases and their corresponding modifications in budding yeast and humans: activities, predications, and potential roles in human health.DNA Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;31(4):434-54. doi: 10.1089/dna.2011.1437. Epub 2011 Dec 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22191691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant translation regulated by METTL1/WDR4-mediated tRNA N7-methylguanosine modification drives head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022 Mar;42(3):223-244. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12273. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35179319 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of N6,N6-dimethyladenosine in transfer RNA from Mycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette-Guérin.Molecules. 2011 Jun 21;16(6):5168-81. doi: 10.3390/molecules16065168. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21694680 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and Validation of the Prognosis ability of the M7GRelated miRNAs in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Apr 1;24(4):1275-1287. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.4.1275. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37116150 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into how WDR4 promotes the tRNA N7-methylguanosine methyltransferase activity of METTL1.Cell Discov. 2023 Jun 27;9(1):65. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00562-y. Cell Discov. 2023. PMID: 37369656 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Codon-biased translation can be regulated by wobble-base tRNA modification systems during cellular stress responses.RNA Biol. 2015;12(6):603-14. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1031947. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25892531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexandrov, A., Vignali, M., LaCount, D.J., Quartley, E., de Vries, C., De Rosa, D., Babulski, J., Mitchell, S.F., Schoenfeld, L.W., Fields, S., et al. 2004. A facile method for high-throughput co-expression of protein pairs. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3: 934–938. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, J., Phan, L., Cuesta, R., Carlson, B.A., Pak, M., Asano, K., Bjork, G.R., Tamame, M., and Hinnebusch, A.G. 1998. The essential Gcd10p-Gcd14p nuclear complex is required for 1-methyl-adenosine modification and maturation of initiator methionyl-tRNA. Genes & Dev. 12: 3650–3662. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
