Simulations of the pressure and temperature unfolding of an alpha-helical peptide
- PMID: 15800045
- PMCID: PMC1100754
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408527102
Simulations of the pressure and temperature unfolding of an alpha-helical peptide
Abstract
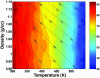
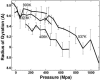
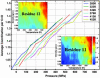
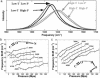
We study by molecular simulations the reversible folding/unfolding equilibrium as a function of density and temperature of a solvated alpha-helical peptide. We use an extension of the replica exchange molecular dynamics method that allows for density and temperature Monte Carlo exchange moves. We studied 360 thermodynamic states, covering a density range from 0.96 to 1.14 g.cm(-3) and a temperature range from 300 to 547.6 K. We simulated 10 ns per replica for a total simulation time of 3.6 micros. We characterize the structural, thermodynamic, and hydration changes as a function of temperature and pressure. We also calculate the compressibility and expansivity of unfolding. We find that pressure does not affect the helix-coil equilibrium significantly and that the volume change upon pressure unfolding is small and negative (-2.3 ml/mol). However, we find significant changes in the coordination of water molecules to the backbone carbonyls. This finding predicts that changes in the chemical shifts and IR spectra with pressure can be due to changes in coordination and not only changes in the helical content. A simulation of the IR spectrum shows that water coordination effects on frequency shifts are larger than changes due to elastic structural changes in the peptide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Equilibrium structure and folding of a helix-forming peptide: circular dichroism measurements and replica-exchange molecular dynamics simulations.Biophys J. 2004 Dec;87(6):3786-98. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.045419. Epub 2004 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 15339816 Free PMC article.
-
Helix-coil transition of alanine peptides in water: force field dependence on the folded and unfolded structures.Proteins. 2005 Jun 1;59(4):773-82. doi: 10.1002/prot.20439. Proteins. 2005. PMID: 15815975
-
Structural analysis of a helical peptide unfolding pathway.Chemistry. 2010 May 10;16(18):5400-7. doi: 10.1002/chem.200903428. Chemistry. 2010. PMID: 20358558
-
Protein folding pathways from replica exchange simulations and a kinetic network model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 10;102(19):6801-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408970102. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15800044 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature and pressure denaturation of chignolin: folding and unfolding simulation by multibaric-multithermal molecular dynamics method.Proteins. 2012 Oct;80(10):2397-416. doi: 10.1002/prot.24125. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 22641605
Cited by
-
High-pressure NMR reveals close similarity between cold and alcohol protein denaturation in ubiquitin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 29;110(5):E368-76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212222110. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23284170 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the energy landscape of protein folding using replica-exchange and conventional molecular dynamics simulations.J Struct Biol. 2007 Mar;157(3):514-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.10.002. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Struct Biol. 2007. PMID: 17113307 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design and experimental discovery of an antiestrogenic peptide derived from alpha-fetoprotein.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 May 16;129(19):6263-8. doi: 10.1021/ja070202w. Epub 2007 Apr 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17441722 Free PMC article.
-
A water-explicit lattice model of heat-, cold-, and pressure-induced protein unfolding.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 15;93(12):4116-27. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.108530. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17766342 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized molecular dynamics force fields applied to the helix-coil transition of polypeptides.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Jul 2;113(26):9004-15. doi: 10.1021/jp901540t. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19514729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gnanakaran, S., Nymeyer, H., Portman, J. J., Sanbonmatsu, K. Y. & Garcia, A. E. (2003) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13, 168–174. - PubMed
-
- Boczko, E. M. & Brooks, C. L., III (1995) Science 269, 393–396. - PubMed
-
- Sugita, Y. & Okamoto, Y. (1999) Chem. Phys. Lett. 314, 141–151.
-
- Hansmann, U. (1997) Chem. Phys. Lett. 281, 140–150.
-
- Hukushima, K. & Nemoto, K. (1996) J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 65, 1604–1608.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

