Peptides derived from apoptotic Bax and Bid reproduce the poration activity of the parent full-length proteins
- PMID: 15778450
- PMCID: PMC1305629
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.058008
Peptides derived from apoptotic Bax and Bid reproduce the poration activity of the parent full-length proteins
Abstract
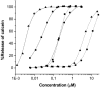
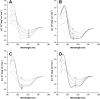
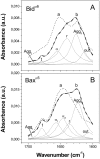
Bax and Bid are proapoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family that regulate the release of apoptogenic factors from mitochondria. Although they localize constitutively in the cytoplasm, their apoptotic function is exerted at the mitochondrial outer membrane, and is related to their ability to form transbilayer pores. Here we report the poration activity of fragments from these two proteins, containing the first alpha-helix of a colicinlike hydrophobic hairpin (alpha-helix 5 of Bax and alpha-helix 6 of Bid). Both peptides readily bind to synthetic lipid vesicles, where they adopt predominantly alpha-helical structures and induce the release of entrapped calcein. In planar lipid membranes they form ion conducting channels, which in the case of the Bax-derived peptide are characterized by a two-stage pattern, a large conductivity and lipid-charge-dependent ionic selectivity. These features, together with the influence of intrinsic lipid curvature on the poration activity and the existence of two helical stretches of different orientations for the membrane-bound peptide, suggest that it forms mixed lipidic/peptidic pores of toroidal structure. In contrast, the assayed Bid fragment shows a markedly different behavior, characterized by the formation of discrete, steplike channels in planar lipid bilayers, as expected for a peptidic pore lined by a bundle of helices.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane-insertion fragments of Bcl-xL, Bax, and Bid.Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 31;43(34):10930-43. doi: 10.1021/bi036044c. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15323553
-
Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family of proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 1;1644(2-3):83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2003.08.012. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 14996493 Review.
-
Peptides corresponding to helices 5 and 6 of Bax can independently form large lipid pores.FEBS J. 2006 Mar;273(5):971-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05123.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16478471
-
Bid induces cytochrome c-impermeable Bax channels in liposomes.Biochem J. 2002 May 1;363(Pt 3):547-52. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3630547. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 11964155 Free PMC article.
-
Bid: a Bax-like BH3 protein.Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1:S93-104. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.47. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641510 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational changes and protein stability of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2009 Feb;41(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s10863-009-9202-1. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2009. PMID: 19255832 Free PMC article.
-
Assembling the puzzle: Oligomerization of α-pore forming proteins in membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1858(3):457-466. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.09.013. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26375417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The secrets of the Bcl-2 family.Cell Death Differ. 2012 Nov;19(11):1733-40. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.105. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Cell Death Differ. 2012. PMID: 22935609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pore formation by a Bax-derived peptide: effect on the line tension of the membrane probed by AFM.Biophys J. 2007 Jul 1;93(1):103-12. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.100370. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17416629 Free PMC article.
-
Bax-derived membrane-active peptides act as potent and direct inducers of apoptosis in cancer cells.J Cell Sci. 2011 Feb 15;124(Pt 4):556-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.076745. Epub 2011 Jan 18. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21245196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. M., and S. Cory. 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, C., M. Dalla Serra, C. Potrich, I. Bernhart, M. Tejuca, D. Martinez, I. F. Pazos, M. E. Lanio, and G. Menestrina. 2001. Effects of lipid composition on membrane permeabilization by Sticholysin I and II, two cytolysins of the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. Biophys. J. 80:2761–2774. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderluh, G., M. Dalla Serra, G. Viero, G. Guella, P. Macek, and G. Menestrina. 2003. Pore formation by equinatoxin II, an eukaryotic protein toxin, occurs by induction of non-lamellar lipid structures. J. Biol. Chem. 278:45216–45223. - PubMed
-
- Antonsson, B., F. Conti, A. Ciavatta, S. Montessuit, S. Lewis, I. Martinou, L. Bernasconi, A. Bernard, J. J. Mermod, G. Mazzei, K. Maundrell, F. Gambale, R. Sadoul, and J. C. Martinou. 1997. Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science. 277:370–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

