Critical role of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-encoded RNA in efficient EBV-induced B-lymphocyte growth transformation
- PMID: 15767430
- PMCID: PMC1061531
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4298-4307.2005
Critical role of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-encoded RNA in efficient EBV-induced B-lymphocyte growth transformation
Abstract
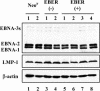
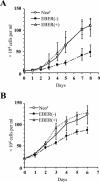
It was demonstrated that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) were nonessential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. We revisited this issue by producing a large quantity of EBER-deleted EBV by using an Akata cell system. Although the EBER-deleted virus efficiently infected B lymphocytes, its 50% transforming dose was approximately 100-fold less than that of the EBER-positive EBV. We then engineered the genome of EBER-deleted virus and generated a recombinant virus with the EBER genes reconstituted at their native locus. The resultant EBER-reconstituted EBV exhibited restored transforming ability. In addition, lymphoblastoid cell lines established with the EBER-deleted EBV grew significantly more slowly than those established with wild-type or EBER-reconstituted EBV, and the difference between the growth rates was especially highlighted when the cells were plated at low cell densities. These results clearly demonstrate that EBERs significantly contribute to the efficient growth transformation of B lymphocytes by enhancing the growth potential of transformed lymphocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA 2 (EBER2) but not EBER1 plays a critical role in EBV-induced B-cell growth transformation.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11236-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00579-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17686859 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus with small RNA (EBER) genes deleted transforms lymphocytes and replicates in vitro.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1546-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1546. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. PMID: 1847527 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent detection of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in peripheral T-cell lymphomas.J Pathol. 1998 May;185(1):79-85. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199805)185:1<79::AID-PATH52>3.0.CO;2-3. J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9713363
-
Regulation and dysregulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency: implications for the development of autoimmune diseases.Autoimmunity. 2008 May;41(4):298-328. doi: 10.1080/08916930802024772. Autoimmunity. 2008. PMID: 18432410 Review.
-
Identification of EBV transforming genes by recombinant EBV technology.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):407-14. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2001.0407. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11669602 Review.
Cited by
-
Extra-telomeric functions of telomerase in the pathogenesis of Epstein-Barr virus-driven B-cell malignancies and potential therapeutic implications.Infect Agent Cancer. 2018 Apr 10;13:14. doi: 10.1186/s13027-018-0186-5. eCollection 2018. Infect Agent Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29643934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of LINC00312, a long intergenic non-coding RNA, is negatively correlated with tumor size but positively correlated with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Mol Histol. 2013 Oct;44(5):545-54. doi: 10.1007/s10735-013-9503-x. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Mol Histol. 2013. PMID: 23529758
-
Virus-Driven Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 27;13(11):2625. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112625. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple domains of EBER 1, an Epstein-Barr virus noncoding RNA, recruit human ribosomal protein L22.RNA. 2006 May;12(5):872-82. doi: 10.1261/rna.2339606. Epub 2006 Mar 23. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16556938 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs produced by oncogenic human herpesviruses.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;216(2):321-6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21480. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18484093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clemens, M. J. 1993. The small RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 17:81-92. - PubMed
-
- Condit, R. C. 2001. Principles of virology, p. 19-51. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, D. E. Griffin, R. A. Lamb, M. A. Martin, B. Roizman, and S. E. Straus (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Eliopoulos, A. G., M. Stack, C. W. Dawson, K. M. Kaye, L. Hodgkin, S. Sihota, M. Rowe, and L. S. Young. 1997. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and CD40 mediate IL-6 production in epithelial cells via an NF-kappaB pathway involving TNF receptor-associated factors. Oncogene 14:2899-2916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

