Pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in subjects with Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis
- PMID: 15752374
- PMCID: PMC1884781
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02251.x
Pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in subjects with Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis
Abstract
Aim: Lipid lowering therapy with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors is increasingly used for the prevention of cardiovascular events, but they should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver function. We therefore studied the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Methods: Plasma concentrations of pitavastatin were determined after administration of 2 mg single-dose pitavastatin to 12 male patients with liver cirrhosis (six Child-Pugh grade A and six grade B). These results were compared with the single-dose pharmacokinetic results obtained from six male volunteers without liver disease.
Results: Administration of 2 mg single-dose pitavastatin to patients with Child-Pugh grade A and grade B cirrhosis resulted in a 1.19- and 2.47-fold increase in Cmax and 1.27- and 3.64-fold increase in AUCt, respectively, when compared with normal subjects. The geomean Cmax of pitavastatin was 59.5 ng ml(-1), 70.7 ng ml(-1) and 147.1 ng ml(-1) in the control, Child-Pugh grade A and Child-Pugh grade B groups, respectively. The geomean AUCt of pitavastatin in the three groups was 121.2 ng h(-1) ml(-1), 154.2 ng h(-1) ml(-1) and 441.7 ng h(-1) ml(-1), respectively. The geomean Cmax of pitavastatin lactone was 20.3 ng ml(-1), 19.1 ng ml(-1) and 9.9 ng ml(-1) in the control, Child-Pugh grade A and grade B groups, respectively. The AUCt of pitavastatin lactone was 120.2 h(-1) ml(-1), 108.8 h(-1) ml(-1) and 87.5 h(-1) ml(-1), respectively.
Conclusion: The plasma concentration of pitavastatin is increased in patients with liver cirrhosis. In such patients, caution is required, although dose reduction may not be necessary in Child-Pugh A cirrhosis.
Figures

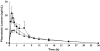
Similar articles
-
Single and repeated dose pharmacokinetics of dexketoprofen trometamol in patients with impaired liver function.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Jun;28 Suppl A:29-36. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16801990 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and safety of bosutinib in patients with chronic hepatic impairment and matched healthy subjects.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;71(1):123-32. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-1987-7. Epub 2012 Sep 30. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23053269 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) variant alleles on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in healthy volunteers.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Oct;78(4):342-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.07.003. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16198653 Clinical Trial.
-
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide in patients with mild and moderate liver cirrhosis.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(5):403-16. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200746050-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007. PMID: 17465639 Clinical Trial.
-
Pitavastatin: a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Mar;44(3):507-14. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M624. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20179258 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane transporters in drug development and as determinants of precision medicine.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Apr;23(4):255-280. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00877-1. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38267543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving about.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Mar;59(3):263-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02399.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15752370 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
ABT-737 and pictilisib synergistically enhance pitavastatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):1979-1984. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7516. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434898 Free PMC article.
-
Pitavastatin: a review of its use in the management of hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia.Drugs. 2012 Mar 5;72(4):565-84. doi: 10.2165/11207180-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22356292 Review.
-
Critical appraisal of the role of pitavastatin in treating dyslipidemias and achieving lipid goals.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5:921-36. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s5551. Epub 2009 Nov 16. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19997573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Consensus conference. Lowering blood cholesterol to prevent heart disease. JAMA. 1985;253:2080–6. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KM, Castelli WP, Levy D Cholesterol. mortality. 30 years of follow-up from the Framingham study. JAMA. 1987;257:2176–80. - PubMed
-
- Frick MH, Elo O, Haapa K, Heinonen OP, Heinsalmi P, Helo P, et al. Helsinki Heart Study: primary-prevention trial with gemfibrozil in middle-aged men with dyslipidemia. Safety of treatment, changes in risk factors, and incidence of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1237–45. - PubMed
-
- Havel RJ, Rapaport E. Management of primary hyperlipidemia. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1491–8. - PubMed
-
- The West Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. A coronary primary prevention study of Scottish men aged 45–64 years: trial design. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:849–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

