NADPH-oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species mediate the cerebrovascular dysfunction induced by the amyloid beta peptide
- PMID: 15716413
- PMCID: PMC6725936
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5207-04.2005
NADPH-oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species mediate the cerebrovascular dysfunction induced by the amyloid beta peptide
Abstract
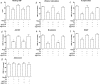
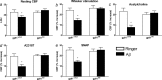
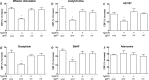
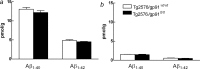
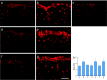
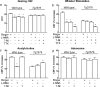
Overproduction of the amyloid beta (Abeta) peptide is a key factor in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the mechanisms of its pathogenic effects have not been defined. Patients with AD have cerebrovascular alterations attributable to the deleterious effects of Abeta on cerebral blood vessels. We report here that NADPH oxidase, the major source of free radicals in blood vessels, is responsible for the cerebrovascular dysregulation induced by Abeta. Thus, the free-radical production and the associated alterations in vasoregulation induced by Abeta are abrogated by the NADPH oxidase peptide inhibitor gp91ds-tat and are not observed in mice lacking the catalytic subunit of NADPH oxidase (gp91phox). Furthermore, oxidative stress and cerebrovascular dysfunction do not occur in transgenic mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein but lacking gp91phox. The mechanisms by which NADPH oxidase-derived radicals mediate the cerebrovascular dysfunction involve reduced bioavailability of nitric oxide. Thus, a gp91phox-containing NADPH oxidase is the critical link between Abeta and cerebrovascular dysfunction, which may underlie the alteration in cerebral blood flow regulation observed in AD patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II impairs neurovascular coupling in neocortex through NADPH oxidase-derived radicals.Circ Res. 2004 Nov 12;95(10):1019-26. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000148637.85595.c5. Epub 2004 Oct 21. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15499027
-
Nox2-derived radicals contribute to neurovascular and behavioral dysfunction in mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 29;105(4):1347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711568105. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18202172 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor CD36 is essential for the cerebrovascular oxidative stress and neurovascular dysfunction induced by amyloid-beta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 22;108(12):5063-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015413108. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21383152 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine residue 35 is critical for the oxidative stress and neurotoxic properties of Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide 1-42.Peptides. 2002 Jul;23(7):1299-309. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(02)00066-9. Peptides. 2002. PMID: 12128086 Review.
-
The role of an astrocytic NADPH oxidase in the neurotoxicity of amyloid beta peptides.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Dec 29;360(1464):2309-14. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1766. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16321801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: the potential of NOX2 inhibitors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(14):2409-27. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1015-4. Epub 2012 May 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22581365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel MRI Techniques Identifying Vascular Leak and Paravascular Flow Reduction in Early Alzheimer Disease.Biomedicines. 2020 Jul 20;8(7):228. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8070228. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32698354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoprotein receptor-related protein-6 protects the brain from ischemic injury.Stroke. 2013 Aug;44(8):2284-2291. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001320. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23743975 Free PMC article.
-
Cessation of neoangiogenesis in Alzheimer's disease follows amyloid-beta immunization.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1354. doi: 10.1038/srep01354. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23446889 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PPARδ prevents endothelial dysfunction induced by overexpression of amyloid-β precursor protein.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Dec 1;96(3):504-12. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs266. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22886847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi T, Weisbrod RM, Pimentel DR, Ying J, Sharov VS, Schoneich C, Cohen RA (2004) S-Glutathiolation by peroxynitrite activates SERCA during arterial relaxation by nitric oxide. Nat Med 10: 1200-1207. - PubMed
-
- Ayata C, Ma J, Meng W, Huang P, Moskowitz MA (1996) L-NA-sensitive rCBF augmentation during vibrissal stimulation in type III nitric oxide synthase mutant mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16: 539-541. - PubMed
-
- Babior BM (2004) NADPH oxidase. Curr Opin Immunol 16: 42-47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
