Parkinson-like syndrome induced by continuous MPTP infusion: convergent roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and alpha-synuclein
- PMID: 15716361
- PMCID: PMC552938
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409713102
Parkinson-like syndrome induced by continuous MPTP infusion: convergent roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and alpha-synuclein
Abstract
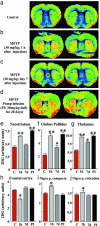
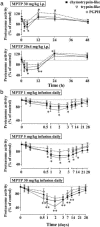
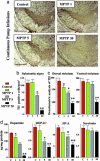
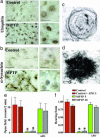
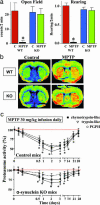
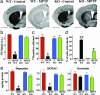
In animals, sporadic injections of the mitochondrial toxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) selectively damage dopaminergic neurons but do not fully reproduce the features of human Parkinson's disease. We have now developed a mouse Parkinson's disease model that is based on continuous MPTP administration with an osmotic minipump and mimics many features of the human disease. Although both sporadic and continuous MPTP administration led to severe striatal dopamine depletion and nigral cell loss, we find that only continuous administration of MPTP produced progressive behavioral changes and triggered formation of nigral inclusions immunoreactive for ubiquitin and alpha-synuclein. Moreover, only continuous MPTP infusions caused long-lasting activation of glucose uptake and inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. In mice lacking alpha-synuclein, continuous MPTP delivery still induced metabolic activation, but induction of behavioral symptoms and neuronal cell death were almost completely alleviated. Furthermore, the inhibition of the ubiquitinproteasome system and the production of inclusion bodies were reduced. These data suggest that continuous low-level exposure of mice to MPTP causes a Parkinson-like syndrome in an alpha-synuclein-dependent manner.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Convergent roles of alpha-synuclein, DA metabolism, and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in nigrostriatal toxicity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1074:84-9. doi: 10.1196/annals.1369.007. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17105905
-
Alpha-synuclein up-regulation in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons following administration of the parkinsonian toxin MPTP.J Neurochem. 2000 Feb;74(2):721-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.740721.x. J Neurochem. 2000. PMID: 10646524
-
Mice lacking alpha-synuclein have an attenuated loss of striatal dopamine following prolonged chronic MPTP administration.Neurotoxicology. 2004 Sep;25(5):761-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2004.05.002. Neurotoxicology. 2004. PMID: 15288507
-
alpha-Synuclein- and MPTP-generated rodent models of Parkinson's disease and the study of extracellular striatal dopamine dynamics: a microdialysis approach.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Aug;9(4):482-90. doi: 10.2174/187152710791556177. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20522009 Review.
-
[Genetics and environmental factors of Parkinson disease].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2002 Dec;158 Spec no 1:S11-23. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2002. PMID: 12690660 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Protein degradation pathways in Parkinson's disease: curse or blessing.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Aug;124(2):153-72. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1004-6. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22744791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of protein quality control in Parkinson's disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 May;2(5):a009423. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009423. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 22553500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalamic degeneration in MPTP-treated Parkinsonian monkeys: impact upon glutamatergic innervation of striatal cholinergic interneurons.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Dec;224(9):3321-3338. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01967-w. Epub 2019 Nov 2. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 31679085 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term RNAi knockdown of α-synuclein in the adult rat substantia nigra without neurodegeneration.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 May;125:146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 30658149 Free PMC article.
-
Radio Signals from Live Cells: The Coming of Age of In-Cell Solution NMR.Chem Rev. 2022 May 25;122(10):9267-9306. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00790. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35061391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dauer, W. & Przedborski, S. (2003) Neuron 39, 889-909. - PubMed
-
- Giasson, B. I. & Lee, V. M. (2003) Cell 114, 1-8. - PubMed
-
- Greenamyre, J. T. & Hastings, T. G. (2004) Science 304, 1120-1122. - PubMed
-
- Lansbury, P. T. & Brice, A. (2002) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 653-660. - PubMed
-
- Heikkila, R. E., Hess, A. & Duvoisin, R. C. (1984) Science 224, 1451-1453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

