Constitutive homing of mast cell progenitors to the intestine depends on autologous expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR2
- PMID: 15705791
- PMCID: PMC1895025
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3578
Constitutive homing of mast cell progenitors to the intestine depends on autologous expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR2
Abstract
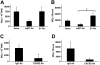
Homing of mast cell progenitors (MCps) to the mouse small intestine involves the interaction of alpha4beta7 integrin with mucosal addressin cellular adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1). We now demonstrate the dependence of this process on CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) using null strains and mice sublethally irradiated and bone marrow (BM) reconstituted (SIBR) with wild-type or null BM or with wild-type BM followed by administration of blocking antibody. The intestinal MCp concentration in CXCR2(-/-) mice was reduced by 67%, but was unaltered in CC chemokine receptor 2(-/-) (CCR2(-/-)), CCR3(-/-), or CCR5(-/-) mice. SIBR mice given CXCR2(-/-) BM had an intestinal MCp concentration that was 76% less than that in BALB/c BM reconstituted mice. Antibody blockade of VCAM-1 or of CXCR2 in SIBR mice reduced intestinal MCp reconstitution, and mice lacking endothelial VCAM-1 also had a marked reduction relative to wild-type mice. Finally, the half-life of intestinal MCps in wild-type mice was less than one week on the basis of a more than 50% reduction by administration of anti-alpha4beta7 integrin or anti-CXCR2. Thus, the establishment and maintenance of MCps in the small intestine is a dynamic process that requires expression of the alpha4beta7 integrin and the alpha-chemokine receptor CXCR2.
Figures
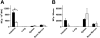
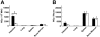
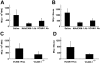
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32851663 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of two major intracellular phospholipases A(2) (PLA(2)) in mast cells reveals crucial contribution of cytosolic PLA(2)α, not Ca(2+)-independent PLA(2)β, to lipid mobilization in proximal mast cells and distal fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 28;286(43):37249-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.290312. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21880721 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR2: From Bench to Bedside.Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 24;3:263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00263. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22936934 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary CXCR2 regulates VCAM-1 and antigen-induced recruitment of mast cell progenitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 18;104(51):20478-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709651104. Epub 2007 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18077323 Free PMC article.
-
Localization-Specific Expression of CCR1 and CCR5 by Mast Cell Progenitors.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 26;11:321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00321. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32174921 Free PMC article.
-
Development of mast cells and importance of their tryptase and chymase serine proteases in inflammation and wound healing.Adv Immunol. 2014;122:211-52. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800267-4.00006-7. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24507159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Enerback L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa: 2, dye-binding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66: 303-312. - PubMed
-
- Gurish MF, Pear WS, Stevens RL, et al. Tissue-regulated differentiation and maturation of a v-abl-immortalized mast cell-committed progenitor. Immunity. 1995;3: 175-186. - PubMed
-
- Andrew DP, Berlin C, Honda S, et al. Distinct but overlapping epitopes are involved in alpha 4 beta 7-mediated adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, mucosal addressin-1, fibronectin, and lymphocyte aggregation. J Immunol. 1994;153: 3847-3861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

