The G protein-coupled receptor Gpr1 and the Galpha protein Gpa2 act through the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway to induce morphogenesis in Candida albicans
- PMID: 15673611
- PMCID: PMC1073676
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0780
The G protein-coupled receptor Gpr1 and the Galpha protein Gpa2 act through the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway to induce morphogenesis in Candida albicans
Abstract
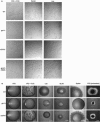
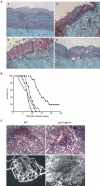
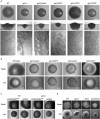
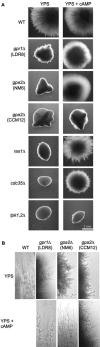
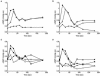
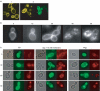
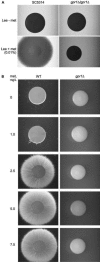
We investigated the role in cell morphogenesis and pathogenicity of the Candida albicans GPR1 gene, encoding the G protein-coupled receptor Gpr1. Deletion of C. albicans GPR1 has only minor effects in liquid hypha-inducing media but results in strong defects in the yeast-to-hypha transition on solid hypha-inducing media. Addition of cAMP, expression of a constitutively active allele of the Galpha protein Gpa2 or of the catalytic protein kinase A subunit TPK1 restores the wild-type phenotype of the CaGPR1-deleted strain. Overexpression of HST7, encoding a component of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, does not suppress the defect in filamentation. These results indicate that CaGpr1 functions upstream in the cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway. We also show that, in the presence of glucose, CaGpr1 is important for amino acid-induced transition from yeast to hyphal cells. Finally, as opposed to previous reports, we show that CaGpa2 acts downstream of CaGpr1 as activator of the cAMP-PKA pathway but that deletion of neither CaGpr1 nor CaGpa2 affects glucose-induced cAMP signaling. In contrast, the latter is abolished in strains lacking CaCdc25 or CaRas1, suggesting that the CaCdc25-CaRas1 rather than the CaGpr1-CaGpa2 module mediates glucose-induced cAMP signaling in C. albicans.
Figures
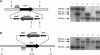
Similar articles
-
Gpr1, a putative G-protein-coupled receptor, regulates morphogenesis and hypha formation in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):919-31. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.4.919-931.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15302825 Free PMC article.
-
GPR1 encodes a putative G protein-coupled receptor that associates with the Gpa2p Galpha subunit and functions in a Ras-independent pathway.EMBO J. 1998 Apr 1;17(7):1996-2007. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.7.1996. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9524122 Free PMC article.
-
Hgc1, a novel hypha-specific G1 cyclin-related protein regulates Candida albicans hyphal morphogenesis.EMBO J. 2004 Apr 21;23(8):1845-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600195. Epub 2004 Apr 8. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15071502 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sensing mechanisms and targets for the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Sep;33(5):904-18. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01538.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10476026 Review.
-
Multiple roles and diverse regulation of the Ras/cAMP/protein kinase A pathway in Candida albicans.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Jan;111(1):6-16. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14148. Epub 2018 Nov 4. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30299574 Review.
Cited by
-
Dimorphism of Trichosporon cutaneum and impact on its lipid production.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Aug 29;12:203. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1543-3. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31485269 Free PMC article.
-
Combined inactivation of the Candida albicans GPR1 and TPS2 genes results in avirulence in a mouse model for systemic infection.Infect Immun. 2008 Apr;76(4):1686-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01497-07. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18268028 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans cell-type switching and functional plasticity in the mammalian host.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017 Feb;15(2):96-108. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.157. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27867199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central Role of the Trehalose Biosynthesis Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Human Fungal Infections: Opportunities and Challenges for Therapeutic Development.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2017 Mar 15;81(2):e00053-16. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00053-16. Print 2017 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28298477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cAMP-independent signal pathways stimulate hyphal morphogenesis in Candida albicans.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Mar;103(5):764-779. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13588. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27888610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alspaugh, J. A., Pukkila-Worley, R., Harashima, T., Cavallo, L. M., Funnell, D., Cox, G. M., Perfect, J. R., Kronstad, J. W., and Heitman, J. (2002). Adenylyl cyclase functions downstream of the Ga protein Gpa1 and controls mating and pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryotic Cell 1, 75-84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beullens, M., Mbonyi, K., Geerts, L., Gladines, D., Detremerie, K., Jans, A. W., and Thevelein, J. M. (1988). Studies on the mechanism of the glucose-induced cAMP signal in glycolysis and glucose repression mutants of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 172, 227-231. - PubMed
-
- Bockmühl, D. P., Krishnamurthy, S., Gerads, M., Sonneborn, A., and Ernst, J. F. (2001). Distinct and redundant roles of the two protein kinase A isoforms Tpk1 and Tpk2 in morphogenesis and growth of Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 42, 1243-1257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

