Neuroinflammation alters the hippocampal pattern of behaviorally induced Arc expression
- PMID: 15659610
- PMCID: PMC6725337
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4469-04.2005
Neuroinflammation alters the hippocampal pattern of behaviorally induced Arc expression
Abstract
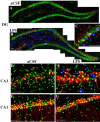
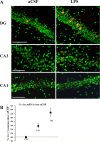
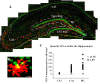
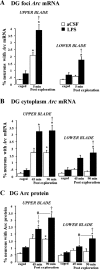
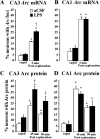
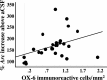
Neuroinflammation is associated with a variety of neurological and pathological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), and is reliably detected by the presence of activated microglia. In early AD, the highest degree of activated microglia is observed in brain regions involved in learning and memory. To investigate whether neuroinflammation alters the pattern of rapid de novo gene expression associated with learning and memory, we studied the expression of the activity-induced immediate early gene Arc in the hippocampus of rats with experimental neuroinflammation. Rats were chronically infused with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (0.25 mug/h) into the fourth ventricle for 28 d. On day 29, the rats explored twice a novel environment for 5 min, separated by 45 or 90 min. In the dentate gyrus and CA3 regions of LPS-infused rats, Arc and OX-6 (specific for major histocompatibility complex class II antigens) immunolabeling and Arc fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed both activated microglia (OX-6 immunoreactivity) and elevated exploration-induced Arc expression compared with control-infused rats. In contrast, in the CA1 of LPS-infused rats, where there was no OX-6 immunostaining, exploration-induced Arc mRNA and protein remained similar in both LPS- and control-infused rats. LPS-induced neuroinflammation did not affect basal levels of Arc expression. Behaviorally induced Arc expression was altered only within the regions showing activated microglia (OX-6 immunoreactivity), suggesting that neuroinflammation may alter the coupling of neural activity with macromolecular synthesis implicated in learning and plasticity. This activity-related alteration in Arc expression induced by neuroinflammation may contribute to the cognitive deficits found in diseases associated with inflammation, such as AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Memantine protects against LPS-induced neuroinflammation, restores behaviorally-induced gene expression and spatial learning in the rat.Neuroscience. 2006 Nov 3;142(4):1303-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.017. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16989956
-
Accuracy of hippocampal network activity is disrupted by neuroinflammation: rescue by memantine.Brain. 2009 Sep;132(Pt 9):2464-77. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp148. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Brain. 2009. PMID: 19531533 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 25;9:23. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-23. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22277195 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic neuroinflammation impacts the recruitment of adult-born neurons into behaviorally relevant hippocampal networks.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Jan;26(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.07.225. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 21787860 Free PMC article.
-
The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: regulation, mechanisms, and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11760-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3864-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Doxycycline-Loaded Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles with a Pectin Coat Can Ameliorate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation Via Enhancing AMPK.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 18;19(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10099-w. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38236457 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota and memory: A symbiotic therapy to counter cognitive decline?Brain Circ. 2019 Sep 30;5(3):124-129. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_34_19. eCollection 2019 Jul-Sep. Brain Circ. 2019. PMID: 31620659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity and implications for future clinical trials.Radiat Oncol J. 2014 Sep;32(3):103-15. doi: 10.3857/roj.2014.32.3.103. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Radiat Oncol J. 2014. PMID: 25324981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Psychological Stress Modulates the Expression of Enzymes Involved in the Kynurenine Pathway throughout Corticolimbic Circuits in Adult Male Rats.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:7215684. doi: 10.1155/2016/7215684. Epub 2015 Dec 27. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26819772 Free PMC article.
-
Short Working Memory Impairment Associated with Hippocampal Microglia Activation in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy.Metabolites. 2024 Mar 29;14(4):193. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040193. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38668321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich B, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WST, Hampel H, Landreth G, McGeer PL, Mrak R, MacKenzie I, O'Banion K, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, et al. (2000) Inflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383-421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albin RL, Greenamyre JT (1992) Alternative excitotoxic hypotheses. Neurology 42: 733-738. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF (2000) Energetics in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 23: 298-304. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF (2003) Mitochondria, oxidative damage, and inflammation in Parkinson's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 991: 120-131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
