3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors attenuate beta-amyloid-induced microglial inflammatory responses
- PMID: 15647473
- PMCID: PMC6725473
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2544-04.2005
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors attenuate beta-amyloid-induced microglial inflammatory responses
Abstract
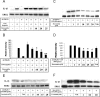
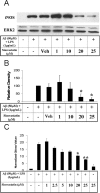
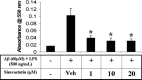
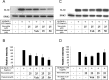
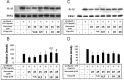
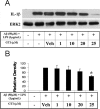
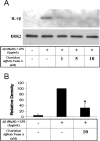
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by extracellular deposits of fibrillar beta-amyloid (Abeta) in the brain, a fulminant microglial-mediated inflammatory reaction, and neuronal death. The use of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins) is associated with a reduced risk of AD, which has been attributed to the cholesterol-lowering actions of these drugs. Statins have been reported recently to have anti-inflammatory actions in addition to their classic lipid-lowering effects. We report that statins robustly inhibited the Abeta-stimulated expression of interleukin-1beta and inducible nitric oxide synthase and the production of nitric oxide by microglia and monocytes. Statin treatment also blocked the rac1-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase and superoxide production. The anti-inflammatory actions of the statins were attributable to their ability to reduce the levels of isoprenyl intermediates in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. The effect of statins could not be reversed by exogenous cholesterol supplementation, indicating that the anti-inflammatory actions are distinct from their cholesterol-lowering actions. The addition of the isoprenyl precursors, mevalonic acid, and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGpp) attenuated the statin-mediated downregulation of inflammatory markers. Prevention of protein isoprenylation by the GGpp transferase inhibitor (GGTI-286) or inhibition of Rho-family function with Clostridium difficile Toxin A blocked the inflammatory response similar to the effect of statin treatment. We argue that the statin-mediated decrease in AD risk arises from their pleiotropic actions, effecting a reduction in neuronal Abeta production and microglia-directed inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of geranylgeranylation mediates the effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors on microglia.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48238-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405442200. Epub 2004 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15364922
-
Simvastatin attenuates expression of cytokine-inducible nitric-oxide synthase in embryonic cardiac myoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 8;280(14):13503-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411859200. Epub 2005 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15705589
-
Statins reduce amyloid-beta production through inhibition of protein isoprenylation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 14;282(37):26832-26844. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702640200. Epub 2007 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17646164
-
Mevalonate Cascade and its Regulation in Cholesterol Metabolism in Different Tissues in Health and Disease.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017;10(1):13-26. doi: 10.2174/1874467209666160112123746. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 26758949 Review.
-
Modulatory effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in diabetic microangiopathy.FASEB J. 2004 May;18(7):805-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0839rev. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15117885 Review.
Cited by
-
Farnesyltransferase haplodeficiency reduces neuropathology and rescues cognitive function in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 13;288(50):35952-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.503904. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24136196 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK and NF-κB pathways are involved in bisphenol A-induced TNF-α and IL-6 production in BV2 microglial cells.Inflammation. 2015 Apr;38(2):637-48. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9971-5. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25047101
-
Simvastatin-mediated enhancement of long-term potentiation is driven by farnesyl-pyrophosphate depletion and inhibition of farnesylation.Neuroscience. 2012 Jan 27;202:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.007. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22192838 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of simvastatin on cholesterol metabolism and Alzheimer disease biomarkers.Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2010 Jul-Sep;24(3):220-6. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0b013e3181d61fea. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2010. PMID: 20473136 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The IFN-gamma-induced transcriptional program of the CIITA gene is inhibited by statins.Eur J Immunol. 2008 Aug;38(8):2325-36. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838189. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18601229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama H, McGeer PL (1990) Brain microglia constitutively express beta-2 integrins. J Neuroimmunol 30: 81-93. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, et al. (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383-421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellosta S, Via D, Canavesi M, Pfister P, Fumagalli R, Paoletti R, Bernini F (1998) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors reduce MMP-9 secretion by macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18: 1671-1678. - PubMed
-
- Blasko I, Apochal A, Boeck G, Hartmann T, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Rans-mayr G (2001) Ibuprofen decreases cytokine-induced amyloid beta production in neuronal cells. Neurobiol Dis 8: 1094-1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
