CD69 expression on CD4+ T lymphocytes after in vitro stimulation with tuberculin is an indicator of immune sensitization against Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens
- PMID: 15642992
- PMCID: PMC540192
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.12.1.101-106.2005
CD69 expression on CD4+ T lymphocytes after in vitro stimulation with tuberculin is an indicator of immune sensitization against Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens
Abstract
The expression of the CD69 antigen on CD4 T lymphocytes after in vitro stimulation with purified protein derivative (2 tuberculin units) was used to evaluate the tuberculin reactivities of 52 individuals from four experimental groups: Mycobacterium bovis BCG-vaccinated healthy individuals with a negative tuberculin skin test (TST) result (group A), BCG-vaccinated healthy individuals with a positive TST result (group B), patients with active tuberculosis (TB) before treatment (group C), and individuals with clinically inactive TB who had previously completed a prescribed course of chemotherapy (group D). The expression of CD69 on CD4 T lymphocytes was significantly higher in patients with active TB (16.2%+/-7.3%), individuals with clinically inactive TB (10.5%+/-7.4%), and healthy individuals with a positive TST result (15.5%+/-7.2%) than in healthy individuals with a negative TST result (3.8%+/-4.3%) (P<0.005). We confirmed the correlation between CD69 antigen expression on T lymphocytes after stimulation with tuberculin and the TST induration diameter (Spearman rho=0.783; P<0.001), an assay for gamma interferon (the Quantiferon-TB assay; Spearman rho=0.613; P<0.001), and the lymphocyte BLAST transformation test (Spearman rho=0.537; P<0.001). Our results demonstrate the usefulness of the determination of CD69 on CD4 T lymphocytes after in vitro stimulation with tuberculin as a rapid indicator of immune sensitization against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Figures
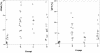
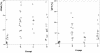

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of an in vitro assay for gamma interferon production in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 Nov;11(6):1089-93. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.6.1089-1093.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15539511 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific CD4- and CD8-positive signatures in different phases of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Mar;75(3):277-81. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.11.023. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23276770
-
Detection by flow cytometry of ESAT-6- and PPD-specific circulating CD4+ T lymphocytes as a diagnostic tool for tuberculosis.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;143(1):1-9. doi: 10.1159/000098220. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17191004
-
[Characteristics of a diagnostic method for tuberculosis infection based on whole blood interferon-gamma assay].Kekkaku. 2006 Nov;81(11):681-6. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17154047 Review. Japanese.
-
[Evolution of IGRA researches].Kekkaku. 2008 Sep;83(9):641-52. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18979999 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Nickel challenge up regulates CD69 expression on T lymphocyte sub-sets from patients with nickel induced contact dermatitis.Afr Health Sci. 2019 Mar;19(1):1460-1466. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v19i1.19. Afr Health Sci. 2019. PMID: 31148973 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Evidence of Human Immune Responsiveness Shows the Improved Potential of a Recombinant BCG Strain for Bladder Cancer Treatment.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1460. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01460. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31297119 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of M. tuberculosis-specific Th1 cells expressing CD69 generated in vivo in pleural fluid cells from patients with tuberculous pleurisy.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023700. Epub 2011 Aug 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887301 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Activation and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Clinically Cured Tuberculosis Are Time-Dependent and Accompanied by Upregulation of IL-10.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 18;8(6):e65492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065492. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23824716 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of CD25, CD69, and CD134 on Tuberculosis-Specific Antigen-Stimulated CD4+ T Cells for Tuberculous Pleurisy.J Immunol Res. 2023 Sep 27;2023:5309816. doi: 10.1155/2023/5309816. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37809012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advisory Council on the Elimination of Tuberculosis. 1999. Tuberculosis elimination revisited: obstacles, opportunities, and a renewed commitment. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 48:1-13. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, American Lung Association, Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2000. Targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161:S221-S247. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, American Lung Association, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2000. Diagnostic standards and classification of tuberculosis in adults and children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161:1376-1395. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, P., A. B. Andersen, A. L. Sorensen, and S. Nagai. 1995. Recall of long-lived immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. J. Immunol. 154:3359-3372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

