Antibodies that are cross-reactive for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade a and clade B v3 domains are common in patient sera from Cameroon, but their neutralization activity is usually restricted by epitope masking
- PMID: 15613306
- PMCID: PMC538589
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.780-790.2005
Antibodies that are cross-reactive for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade a and clade B v3 domains are common in patient sera from Cameroon, but their neutralization activity is usually restricted by epitope masking
Abstract
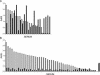
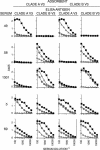
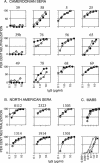
Sera from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected North American patients recognized a fusion protein expressing a V3 loop from a clade B primary isolate virus (JR-CSF) but not from a clade A primary isolate virus (92UG037.8), while most sera from Cameroonian patients recognized both fusion proteins. Competition studies of consensus V3 peptides demonstrated that the majority of the cross-reactive Cameroonian sera contained cross-reactive antibodies that reacted strongly with both V3 sequences. V3-specific antibodies purified from all six cross-reactive sera examined had potent neutralizing activity for virus pseudotyped with envelope proteins (Env) from SF162, a neutralization-sensitive clade B primary isolate. For four of these samples, neutralization of SF162 pseudotypes was blocked by both the clade A and clade B V3 fusion proteins, indicating that this activity was mediated by cross-reactive antibodies. In contrast, the V3-reactive antibodies from only one of these six sera had significant neutralizing activity against viruses pseudotyped with Envs from typically resistant clade B (JR-FL) or clade A (92UG037.8) primary isolates. However, the V3-reactive antibodies from these cross-reactive Cameroonian sera did neutralize virus pseudotyped with chimeric Envs containing the 92UG037.8 or JR-FL V3 sequence in Env backbones that did not express V1/V2 domain masking of V3 epitopes. These data indicated that Cameroonian sera frequently contain cross-clade reactive V3-directed antibodies and indicated that the typical inability of such antibodies to neutralize typical, resistant primary isolate Env pseudotypes was primarily due to indirect masking effects rather than to the absence of the target epitopes.
Figures
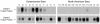
Similar articles
-
The V1/V2 domain of gp120 is a global regulator of the sensitivity of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates to neutralization by antibodies commonly induced upon infection.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):5205-15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5205-5215.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15113902 Free PMC article.
-
The C108g epitope in the V2 domain of gp120 functions as a potent neutralization target when introduced into envelope proteins derived from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):6909-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.6909-6917.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890930 Free PMC article.
-
V3-specific polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from sera of infected humans effectively neutralize primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001 Dec 10;17(18):1737-48. doi: 10.1089/08892220152741432. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001. PMID: 11788025
-
Presentation of native epitopes in the V1/V2 and V3 regions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 by fusion glycoproteins containing isolated gp120 domains.J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):400-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.1.400-410.1994. J Virol. 1994. PMID: 7504740 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of HIV-1: a paradox of humoral proportions.FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2437-55. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712328. FASEB J. 1991. PMID: 1712328 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved structural elements in the V3 crown of HIV-1 gp120.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Aug;17(8):955-61. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1861. Epub 2010 Jul 11. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20622876
-
Partial rescue of V1V2 mutant infectivity by HIV-1 cell-cell transmission supports the domain's exceptional capacity for sequence variation.Retrovirology. 2014 Sep 25;11:75. doi: 10.1186/s12977-014-0075-y. Retrovirology. 2014. PMID: 25287422 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Structural Determinants in MW965 Env That Regulate the Neutralization Phenotype and Conformational Masking Potential of Primary HIV-1 Isolates.J Virol. 2018 Feb 12;92(5):e01779-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01779-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29237828 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble CD4 broadens neutralization of V3-directed monoclonal antibodies and guinea pig vaccine sera against HIV-1 subtype B and C reference viruses.Virology. 2008 Oct 25;380(2):285-95. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18804254 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibody responses to subtype B and C adjuvanted HIV envelope protein vaccination in rabbits.Virology. 2009 Apr 25;387(1):147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.02.005. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19249806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, J., J. Sidney, S. Southwood, J. Ruppert, C. Oseroff, A. Maewal, K. Snoke, H. M. Serra, R. T. Kubo, and A. Sette. 1994. Development of high potency universal DR-restricted helper epitopes by modification of high affinity DR-blocking peptides. Immunity 1:751-761. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2004. 2004 Report on the global HIV/AIDS epidemic: 4th global report. Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Barin, F., Y. Lahbabi, L. Buzelay, B. Lejeune, A. Baillou-Beaufils, F. Denis, C. Mathiot, S. M'Boup, V. Vithayasai, U. Dietrich, and A. Goudeau. 1996. Diversity of antibody binding to V3 peptides representing consensus sequences of HIV type 1 genotypes A to E: an approach for HIV type 1 serological subtyping. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 12:1279-1289. - PubMed
-
- Beirnaert, E., P. Nyambi, B. Willems, L. Heyndrickx, R. Colebunders, W. Janssens, and G. van der Groen. 2000. Identification and characterization of sera from HIV-infected individuals with broad cross-neutralizing activity against group M (env clade A-H) and group O primary HIV-1 isolates. J. Med. Virol. 62:14-24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

