A simple and non-radioactive technique to study the effect of monophosphoesters on matrix vesicle-mediated calcification
- PMID: 15605107
- PMCID: PMC535922
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo97
A simple and non-radioactive technique to study the effect of monophosphoesters on matrix vesicle-mediated calcification
Abstract
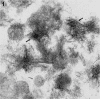
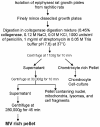
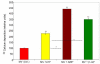
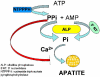
A simple and non-radioactive technique based on O-cresolpthalein complexone assay was developed to study in vitro non-radioactive calcium ((40)Ca) deposition by isolated matrix vesicles. Using this technique, the effect of various phosphoester substrates including ATP, AMP and beta-GP on in vitro MV-calcification was studied. O-cresolpthalein complexone assay with non-radioactive calcium demonstrated that AMP or beta-GP were more effective in promoting calcium deposition by isolated MVs than ATP. The application of this non-radioactive technique, which is highly sensitive and simple, would offer a useful alternative approach to the routinely used radiometric biomineralization assay which employs radioactive (45)Ca.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A simple and defined method to study calcification by isolated matrix vesicles. Effect of ATP and vesicle phosphatase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):162-72. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90056-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977. PMID: 200279
-
Further characterization of ATP-initiated calcification by matrix vesicles isolated from rachitic rat cartilage. Membrane perturbation by detergents and deposition of calcium pyrophosphate by rachitic matrix vesicles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Jan 12;1416(1-2):320-32. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(98)00235-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 9889389
-
Nature of phosphate substrate as a major determinant of mineral type formed in matrix vesicle-mediated in vitro mineralization: An FTIR imaging study.Bone. 2006 Jun;38(6):811-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2005.11.027. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Bone. 2006. PMID: 16461032
-
Involvement of cellular metabolism of calcium and phosphate in calcification of avian growth plate cartilage.J Nutr. 1993 Feb;123(2 Suppl):301-9. doi: 10.1093/jn/123.suppl_2.301. J Nutr. 1993. PMID: 8429379 Review.
-
Matrix vesicles and calcification.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2003 Jun;5(3):222-6. doi: 10.1007/s11926-003-0071-z. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2003. PMID: 12744815 Review.
Cited by
-
End stage renal disease-induced hypercalcemia may promote aortic valve calcification via Annexin VI enrichment of valve interstitial cell derived-matrix vesicles.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Nov;232(11):2985-2995. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25935. Epub 2017 May 24. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28369848 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane vesicles nucleate mineralo-organic nanoparticles and induce carbonate apatite precipitation in human body fluids.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30571-30584. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492157. Epub 2013 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23990473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Synaptotagmin VII regulates bone remodeling by modulating osteoclast and osteoblast secretion.Dev Cell. 2008 Jun;14(6):914-25. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.03.022. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18539119 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix vesicles are carriers of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and noncollagenous matrix proteins.J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(5):514-9. doi: 10.1007/s00774-008-0859-z. Epub 2008 Aug 30. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008. PMID: 18758911
-
Kinetic analysis of substrate utilization by native and TNAP-, NPP1-, or PHOSPHO1-deficient matrix vesicles.J Bone Miner Res. 2010 Apr;25(4):716-23. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.091023. J Bone Miner Res. 2010. PMID: 19874193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson HC. Molecular biology of matrix vesicles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;314:266–280. - PubMed
-
- Anderson HC, Garimella R, Tague SE. The role of matrix vesicles in growth plate development and biomineralization. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2005;10:822–837. - PubMed
-
- Dhanyamraju R, Sipe JB, Anderson HC. Chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of primary cultures of rat growth plate chondrocytes. J Bone Min Res. 2000;15(Suppl 1):S381–S381.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

