Pregnenolone-16alpha-carbonitrile inhibits rodent liver fibrogenesis via PXR (pregnane X receptor)-dependent and PXR-independent mechanisms
- PMID: 15595924
- PMCID: PMC1134989
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041598
Pregnenolone-16alpha-carbonitrile inhibits rodent liver fibrogenesis via PXR (pregnane X receptor)-dependent and PXR-independent mechanisms
Abstract
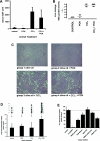
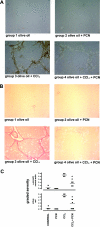
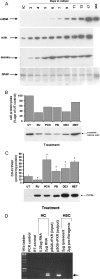
The effect of liver growth stimulation [using the rodent PXR (pregnane X receptor) activator PCN (pregnenolone-16alpha-carbonitrile)] in rats chronically treated with carbon tetrachloride to cause repeated hepatocyte necrosis and liver fibrogenesis was examined. PCN did not inhibit the hepatotoxicity of carbon tetrachloride. However, transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells and the extent of fibrosis caused by carbon tetrachloride treatment was significantly inhibited by PCN in vivo. In vitro, PCN directly inhibited hepatic stellate cell transdifferentiation to a profibrogenic phenotype, although the cells did not express the PXR (in contrast with hepatocytes), suggesting that PCN acts independently of the PXR. Mice with a functionally disrupted PXR gene (PXR-/-) did not respond to the antifibrogenic effects of PCN, in contrast with wild-type (PXR+/+) mice, demonstrating an antifibrogenic role for the PXR in vivo. However, PCN inhibited the transdifferentiation of PXR-/--derived mouse hepatic stellate cells in vitro, confirming that there is also a PXR-independent antifibrogenic effect of PCN through a direct interaction with hepatic stellate cells. These data suggest that the PXR is antifibrogenic in rodents in vivo and that a PXR-independent target for PXR activators exists in hepatic stellate cells that also functions to inhibit fibrosis.
Figures
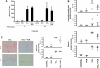

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the hepatic and thyroid gland effects of sodium phenobarbital in wild type and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) knockout rats and pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile in wild type and pregnane X receptor (PXR) knockout rats.Toxicology. 2018 May 1;400-401:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Toxicology. 2018. PMID: 29548889
-
Comparison of the hepatic and thyroid gland effects of sodium phenobarbital and pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile in wild-type and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR)/pregnane X receptor (PXR) knockout rats.Xenobiotica. 2019 Feb;49(2):227-238. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2018.1437300. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Xenobiotica. 2019. PMID: 29424600
-
Coordinate regulation of xenobiotic and bile acid homeostasis by pregnane X receptor.Drug Metab Dispos. 2001 Nov;29(11):1467-72. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001. PMID: 11602523
-
Pregnenolone 16α-carbonitrile ameliorates concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice independent of the nuclear receptor PXR activation.Toxicol Lett. 2017 Apr 5;271:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.02.018. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28237809
-
A mechanism for the anti-fibrogenic effects of the pregnane X receptor (PXR) in the liver: inhibition of NF-kappaB?Toxicology. 2008 Apr 3;246(1):40-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.12.008. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18194834 Review.
Cited by
-
The protective role of pregnane X receptor in lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury.Lab Invest. 2010 Feb;90(2):257-65. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.129. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 19997066 Free PMC article.
-
PXR: a xenobiotic receptor of diverse function implicated in pharmacogenetics.Pharmacogenomics. 2008 Nov;9(11):1695-709. doi: 10.2217/14622416.9.11.1695. Pharmacogenomics. 2008. PMID: 19018724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in cholestatic liver diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;156(1):7-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00030.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19133988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential for cardiac toxicity with methylimidazolium ionic liquids.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Jan 1;249:114439. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114439. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 37272551 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of B-13 progenitor-derived hepatocytes in hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity studies.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Feb;137(2):350-70. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft258. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24235770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman S. L. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:2247–2250. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R., Brenner D. A. Hepatic stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2001;21:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Fausto N., Campbell J. S. The role of hepatocytes and oval cells in liver regeneration and repopulation. Mech. Dev. 2003;120:117–130. - PubMed
-
- Costa R. H., Kalinichenko V. V., Holterman A. X., Wang X. Transcription factors in liver development, differentiation, and regeneration. Hepatology. 2003;38:1331–1347. - PubMed
-
- Gines P., Cardenas A., Arroyo V., Rodes J. Management of cirrhosis and ascites. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:1646–1654. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

