Multiple regulation by calcium of murine homologues of transient receptor potential proteins TRPC6 and TRPC7 expressed in HEK293 cells
- PMID: 15579537
- PMCID: PMC1665365
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.075051
Multiple regulation by calcium of murine homologues of transient receptor potential proteins TRPC6 and TRPC7 expressed in HEK293 cells
Abstract
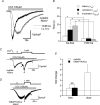
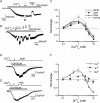
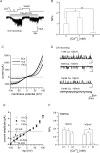
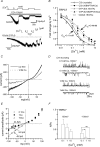
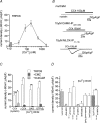
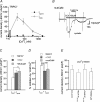
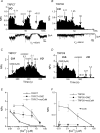
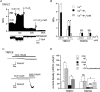
We investigated, by using the patch clamp technique, Ca2+-mediated regulation of heterologously expressed TRPC6 and TRPC7 proteins in HEK293 cells, two closely related homologues of the transient receptor potential (TRP) family and molecular candidates for native receptor-operated Ca2+ entry channels. With nystatin-perforated recording, the magnitude and time courses of activation and inactivation of carbachol (CCh; 100 microM)-activated TRPC6 currents (I(TRPC6)) were enhanced and accelerated, respectively, by extracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+(o)) whether it was continuously present or applied after receptor stimulation. In contrast, Ca2+(o) solely inhibited TRPC7 currents (I(TRPC7)). Vigorous buffering of intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+(i)) under conventional whole-cell clamp abolished the slow potentiating (i.e. accelerated activation) and inactivating effects of Ca2+(o), disclosing fast potentiation (EC50: approximately 0.4 mM) and inhibition (IC50: approximately 4 mM) of I(TRPC6) and fast inhibition (IC50: approximately 0.4 mM) of I(TRPC7). This inhibition of I(TRPC6) and I(TRPC7) seems to be associated with voltage-dependent reductions of unitary conductance and open probability at the single channel level, whereas the potentiation of I(TRPC6) showed little voltage dependence and was mimicked by Sr2+ but not Ba2+. The activation process of I(TRPC6) or its acceleration by Ca2+(o) probably involves phosphorylation by calmodulin (CaM)-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), as pretreatment with calmidazolium (3 microM), coexpression of Ca2+-insensitive mutant CaM, and intracellular perfusion of the non-hydrolysable ATP analogue AMP-PNP and a CaMKII-specific inhibitory peptide all effectively prevented channel activation. However, this was not observed for TRPC7. Instead, single CCh-activated TRPC7 channel activity was concentration-dependently suppressed by nanomolar Ca2+(i) via CaM and conversely enhanced by IP3. In addition, the inactivation time course of I(TRPC6) was significantly retarded by pharmacological inhibition of protein kinase C (PKC). These results collectively suggest that TRPC6 and 7 channels are multiply regulated by Ca2+ from both sides of the membrane through differential Ca2+-CaM-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Figures
Comment in
-
Activation of TRPC6 channel proteins: evidence for an essential role of phosphorylation.J Physiol. 2004 Dec 1;561(Pt 2):354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.077131. Epub 2004 Oct 15. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15489249 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Myosin light chain kinase-independent inhibition by ML-9 of murine TRPC6 channels expressed in HEK293 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;152(1):122-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707368. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17603544 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromultimeric TRPC6-TRPC7 channels contribute to arginine vasopressin-induced cation current of A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2006 Jun 23;98(12):1520-7. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000226495.34949.28. Epub 2006 May 11. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16690880
-
Canonical transient receptor potential TRPC7 can function as both a receptor- and store-operated channel in HEK-293 cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Dec;287(6):C1709-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00350.2004. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15342342
-
Signalling mechanisms for TRPC3 channels.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:123-33; discussion 133-9, 155-9, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104179 Review.
-
Activation, subunit composition and physiological relevance of DAG-sensitive TRPC proteins.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:103-18; discussion 118-22, 155-9, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104178 Review.
Cited by
-
Signal transduction pathways and gating mechanisms of native TRP-like cation channels in vascular myocytes.J Physiol. 2006 Jan 1;570(Pt 1):45-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.096875. Epub 2005 Sep 29. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16195316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Facilitatory effect of Ins(1,4,5)P3 on store-operated Ca2+-permeable cation channels in rabbit portal vein myocytes.J Physiol. 2005 Jul 1;566(Pt 1):161-71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.088260. Epub 2005 Apr 28. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15860523 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II activates two cation conductances with distinct TRPC1 and TRPC6 channel properties in rabbit mesenteric artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2006 Dec 1;577(Pt 2):479-95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119305. Epub 2006 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16973707 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP activates TRPC6 channels via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (PKB)-mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)-ERK1/2 signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19439-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.210294. Epub 2011 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21487005 Free PMC article.
-
Orai1 calcium channels in the vasculature.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Apr;463(5):635-47. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1090-2. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 22402985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boulay G. Ca2+-calmodulin regulates receptor-operated Ca2+ entry activity of TRPC6 in HEK-293 cells. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:201–207. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Brown DM, Qin N, Jiang M, Dietrich A, Zhu MX, Chen Z, Birnbaumer M, Mikoshiba K, Birnbaumer L. Modulation of Ca2+ entry by polypeptides of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) that bind transient receptor potential (TRP): evidence for roles of TRP and IP3R in store depletion-activated Ca2+ entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:14955–14960. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

