EFICAz: a comprehensive approach for accurate genome-scale enzyme function inference
- PMID: 15576349
- PMCID: PMC535665
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh956
EFICAz: a comprehensive approach for accurate genome-scale enzyme function inference
Abstract
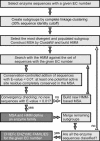
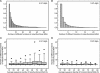
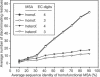
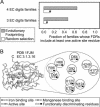
EFICAz (Enzyme Function Inference by Combined Approach) is an automatic engine for large-scale enzyme function inference that combines predictions from four different methods developed and optimized to achieve high prediction accuracy: (i) recognition of functionally discriminating residues (FDRs) in enzyme families obtained by a Conservation-controlled HMM Iterative procedure for Enzyme Family classification (CHIEFc), (ii) pairwise sequence comparison using a family specific Sequence Identity Threshold, (iii) recognition of FDRs in Multiple Pfam enzyme families, and (iv) recognition of multiple Prosite patterns of high specificity. For FDR (i.e. conserved positions in an enzyme family that discriminate between true and false members of the family) identification, we have developed an Evolutionary Footprinting method that uses evolutionary information from homofunctional and heterofunctional multiple sequence alignments associated with an enzyme family. The FDRs show a significant correlation with annotated active site residues. In a jackknife test, EFICAz shows high accuracy (92%) and sensitivity (82%) for predicting four EC digits in testing sequences that are <40% identical to any member of the corresponding training set. Applied to Escherichia coli genome, EFICAz assigns more detailed enzymatic function than KEGG, and generates numerous novel predictions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EFICAz2: enzyme function inference by a combined approach enhanced by machine learning.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Apr 13;10:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-107. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19361344 Free PMC article.
-
How well is enzyme function conserved as a function of pairwise sequence identity?J Mol Biol. 2003 Oct 31;333(4):863-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.08.057. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14568541
-
High precision multi-genome scale reannotation of enzyme function by EFICAz.BMC Genomics. 2006 Dec 13;7:315. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-315. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 17166279 Free PMC article.
-
Using evolutionary information to find specificity-determining and co-evolving residues.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:421-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381538 Review.
-
A Survey for Predicting Enzyme Family Classes Using Machine Learning Methods.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(5):540-550. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666181002143355. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30277150 Review.
Cited by
-
ModEnzA: Accurate Identification of Metabolic Enzymes Using Function Specific Profile HMMs with Optimised Discrimination Threshold and Modified Emission Probabilities.Adv Bioinformatics. 2011;2011:743782. doi: 10.1155/2011/743782. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Adv Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21541071 Free PMC article.
-
The genome of Onchocerca volvulus, agent of river blindness.Nat Microbiol. 2016 Nov 21;2:16216. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.216. Nat Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27869790 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and dynamics of membrane protein in SARS-CoV-2.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Jul;40(10):4725-4738. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1861983. Epub 2020 Dec 22. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33353499 Free PMC article.
-
Is protein classification necessary? Toward alternative approaches to function annotation.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Jun;19(3):363-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19269161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting genes for orphan metabolic activities using phylogenetic profiles.Genome Biol. 2006;7(2):R17. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-2-r17. Epub 2006 Feb 15. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orengo C.A., Todd,A.E. and Thornton,J.M. (1999) From protein structure to function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 9, 374–382. - PubMed
-
- Kenyon G.L., DeMarini,D.M., Fuchs,E., Galas,D.J., Kirsch,J.F., Leyh,T.S., Moos,W.H., Petsko,G.A., Ringe,D., Rubin,G.M. et al. (2002) Defining the mandate of proteomics in the post-genomics era: workshop report. Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 1, 763–780. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez-Sanchez G., Childs,B. and Valle,D. (2001) Human disease genes. Nature, 409, 853–855. - PubMed
-
- Pearson W.R. (2000) Flexible sequence similarity searching with the FASTA3 program package. Methods Mol. Biol., 132, 185–219. - PubMed

