Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early 1 protein facilitates viral replication by antagonizing histone deacetylation
- PMID: 15572445
- PMCID: PMC535392
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407933101
Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early 1 protein facilitates viral replication by antagonizing histone deacetylation
Abstract
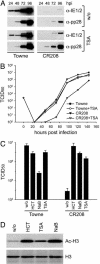
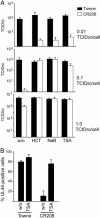
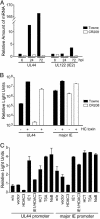
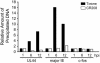
The human cytomegalovirus 72-kDa immediate-early (IE)1 and 86-kDa IE2 proteins are expressed at the start of infection, and they are believed to exert much of their function through promiscuous transcriptional activation of viral and cellular gene expression. Here, we show that the impaired growth of an IE1-deficient mutant virus in human fibroblasts is efficiently rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors of three distinct chemical classes. In the absence of IE1 expression, the viral major IE and UL44 early promoters exhibited decreased de novo acetylation of histone H4 during the early phase of infection, and the hypoacetylation correlated with reduced transcription and accumulation of the respective gene products. Consistent with these findings, IE1 interacts specifically with HDAC3 within infected cells. We also demonstrate an interaction between IE2 and HDAC3. We propose that the ability to modify chromatin is fundamental to transcriptional activation by IE1 and, likely, IE2 as well.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylases in herpesvirus replication and virus-stimulated host defense.Viruses. 2013 Jun 27;5(7):1607-32. doi: 10.3390/v5071607. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23807710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional interaction of the human cytomegalovirus IE2 protein with histone deacetylase 2 in infected human fibroblasts.J Gen Virol. 2007 Dec;88(Pt 12):3214-3223. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.83171-0. J Gen Virol. 2007. PMID: 18024889
-
SUMOylation of the human cytomegalovirus 72-kilodalton IE1 protein facilitates expression of the 86-kilodalton IE2 protein and promotes viral replication.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7803-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7803-7812.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220454 Free PMC article.
-
Exon 3 of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early region is required for efficient viral gene expression and for cellular cyclin modulation.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7438-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7438-7452.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919900 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of the human cytomegalovirus essential IE86 protein.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:133-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77349-8_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18637504 Review.
Cited by
-
Snapshots: chromatin control of viral infection.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):141-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.023. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylases in herpesvirus replication and virus-stimulated host defense.Viruses. 2013 Jun 27;5(7):1607-32. doi: 10.3390/v5071607. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23807710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ICP0 and the US3 protein kinase of herpes simplex virus 1 independently block histone deacetylation to enable gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 27;103(26):9993-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604142103. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16785443 Free PMC article.
-
UL26-deficient human cytomegalovirus produces virions with hypophosphorylated pp28 tegument protein that is unstable within newly infected cells.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3541-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3541-3548.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537622 Free PMC article.
-
The late promoter of the human cytomegalovirus viral DNA polymerase processivity factor has an impact on delayed early and late viral gene products but not on viral DNA synthesis.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6197-206. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00089-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17409154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pass, R. F. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M., Howley, P. M., Griffin, D. E., Lamb, R. A., Martin, M. A., Roizman, B. & Strauss, S. E. (Lippincott, Philadelphia), Vol. 2, pp. 2675–2705.
-
- Mocarski, E. S. & Courcelle, C. T. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M., Howley, P. M., Griffin, D. E., Lamb, R. A., Martin, M. A., Roizman, B. & Strauss, S. E. (Lippincott, Philadelphia), Vol. 2, pp. 2629–2673.
-
- Castillo, J. P. & Kowalik, T. F. (2002) Gene 290, 19–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

