Assembly and budding of influenza virus
- PMID: 15567494
- PMCID: PMC7172797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.08.012
Assembly and budding of influenza virus
Abstract
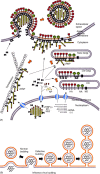
Influenza viruses are causative agents of an acute febrile respiratory disease called influenza (commonly known as "flu") and belong to the Orthomyxoviridae family. These viruses possess segmented, negative stranded RNA genomes (vRNA) and are enveloped, usually spherical and bud from the plasma membrane (more specifically, the apical plasma membrane of polarized epithelial cells). Complete virus particles, therefore, are not found inside infected cells. Virus particles consist of three major subviral components, namely the viral envelope, matrix protein (M1), and core (viral ribonucleocapsid [vRNP]). The viral envelope surrounding the vRNP consists of a lipid bilayer containing spikes composed of viral glycoproteins (HA, NA, and M2) on the outer side and M1 on the inner side. Viral lipids, derived from the host plasma membrane, are selectively enriched in cholesterol and glycosphingolipids. M1 forms the bridge between the viral envelope and the core. The viral core consists of helical vRNP containing vRNA (minus strand) and NP along with minor amounts of NEP and polymerase complex (PA, PB1, and PB2). For viral morphogenesis to occur, all three viral components, namely the viral envelope (containing lipids and transmembrane proteins), M1, and the vRNP must be brought to the assembly site, i.e. the apical plasma membrane in polarized epithelial cells. Finally, buds must be formed at the assembly site and virus particles released with the closure of buds. Transmembrane viral proteins are transported to the assembly site on the plasma membrane via the exocytic pathway. Both HA and NA possess apical sorting signals and use lipid rafts for cell surface transport and apical sorting. These lipid rafts are enriched in cholesterol, glycosphingolipids and are relatively resistant to neutral detergent extraction at low temperature. M1 is synthesized on free cytosolic polyribosomes. vRNPs are made inside the host nucleus and are exported into the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore with the help of M1 and NEP. How M1 and vRNPs are directed to the assembly site on the plasma membrane remains unclear. The likely possibilities are that they use a piggy-back mechanism on viral glycoproteins or cytoskeletal elements. Alternatively, they may possess apical determinants or diffuse to the assembly site, or a combination of these pathways. Interactions of M1 with M1, M1 with vRNP, and M1 with HA and NA facilitate concentration of viral components and exclusion of host proteins from the budding site. M1 interacts with the cytoplasmic tail (CT) and transmembrane domain (TMD) of glycoproteins, and thereby functions as a bridge between the viral envelope and vRNP. Lipid rafts function as microdomains for concentrating viral glycoproteins and may serve as a platform for virus budding. Virus bud formation requires membrane bending at the budding site. A combination of factors including concentration of and interaction among viral components, increased viscosity and asymmetry of the lipid bilayer of the lipid raft as well as pulling and pushing forces of viral and host components are likely to cause outward curvature of the plasma membrane at the assembly site leading to bud formation. Eventually, virus release requires completion of the bud due to fusion of the apposing membranes, leading to the closure of the bud, separation of the virus particle from the host plasma membrane and release of the virus particle into the extracellular environment. Among the viral components, M1 contains an L domain motif and plays a critical role in budding. Bud completion requires not only viral components but also host components. However, how host components facilitate bud completion remains unclear. In addition to bud completion, influenza virus requires NA to release virus particles from sialic acid residues on the cell surface and spread from cell to cell. Elucidation of both viral and host factors involved in viral morphogenesis and budding may lead to the development of drugs interfering with the steps of viral morphogenesis and in disease progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influenza virus morphogenesis and budding.Virus Res. 2009 Aug;143(2):147-61. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.05.010. Epub 2009 May 27. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 19481124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transport of viral proteins to the apical membranes and interaction of matrix protein with glycoproteins in the assembly of influenza viruses.Virus Res. 2001 Sep;77(1):61-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(01)00266-0. Virus Res. 2001. PMID: 11451488 Review.
-
Influenza A virus hemagglutinin and neuraminidase mutually accelerate their apical targeting through clustering of lipid rafts.J Virol. 2014 Sep 1;88(17):10039-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00586-14. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24965459 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral Organization of Influenza Virus Proteins in the Budozone Region of the Plasma Membrane.J Virol. 2017 Apr 13;91(9):e02104-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02104-16. Print 2017 May 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28202765 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza virus assembly: effect of influenza virus glycoproteins on the membrane association of M1 protein.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(18):8709-19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8709-8719.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10954572 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of influenza A M2 transmembrane domain assembly in lipid membranes.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 20;5:11757. doi: 10.1038/srep11757. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26190831 Free PMC article.
-
A second CRM1-dependent nuclear export signal in the influenza A virus NS2 protein contributes to the nuclear export of viral ribonucleoproteins.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(2):767-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06519-11. Epub 2012 Oct 31. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23115280 Free PMC article.
-
Bending-driven patterning of solid inclusions in lipid membranes: Colloidal assembly and transitions in elastic 2D fluids.PNAS Nexus. 2024 Aug 7;3(8):pgae331. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae331. eCollection 2024 Aug. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 39211516 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A: understanding the viral life cycle.Yale J Biol Med. 2009 Dec;82(4):153-9. Yale J Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20027280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breathing and tilting: mesoscale simulations illuminate influenza glycoprotein vulnerabilities.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Aug 7:2022.08.02.502576. doi: 10.1101/2022.08.02.502576. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: ACS Cent Sci. 2022 Dec 28;8(12):1646-1663. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c00981. PMID: 35982676 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arzt S., Baudin F., Barge A., Timmins P., Burmeister W.P., Ruigrok R.W.H. Combined results from solution studies on intact influenza virus M1 protein and from a new crystal form of its N-terminal domain show that M1 is an elongated monomer. Virology. 2001;279(2):439–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

