Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro
- PMID: 15548370
- PMCID: PMC1531665
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04241
Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro
Abstract
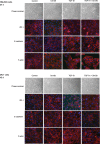
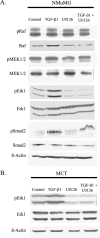
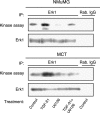
Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) can be tumor-suppressive through the activation of the Smad-mediated signaling pathway. TGF-beta1 can also enhance tumor progression by stimulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through additional pathways. EMT is characterized by the acquisition of a fibroblast-like cell morphology, dissolution of tight junctions, disruption of adherence junctions, and formation of actin stress fibers. There is evidence linking the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways to the induction of TGF-beta1-mediated EMT. However, the role of Erk in the induction of TGF-beta1-mediated EMT remains unclear. TGF-beta1 treatment of normal murine mammary gland (NMuMG) epithelial cells resulted in increased gene expression of Ras, Raf, MEK1/2, and Erk1/2, as shown by microarray analysis and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Upon 24 and 48 hours of treatment with TGF-beta1, NMuMG and mouse cortical tubule (MCT) epithelial cells underwent EMT as shown by changes in cell morphology, delocalization of zonula occludens-1 and E-cadherin from cell-cell junctions, and formation of actin stress fibers. TGF-beta1 treatment also resulted in increased levels of phosphorylated Erk and Erk kinase activity. Treatment with an MEK inhibitor, U0126, inhibited increased Erk phosphorylation and kinase activity, and blocked TGF-beta1-induced EMT in both cell lines. These data show that TGF-beta1 induces the activation of the Erk signaling pathway, which is required for TGF-beta1-mediated EMT in vitro.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Mar;16(3):667-75. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004050425. Epub 2005 Jan 26. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15677311
-
Transforming growth factor beta1 treatment leads to an epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of pancreatic cancer cells requiring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation.Cancer Res. 2001 May 15;61(10):4222-8. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11358848
-
Src activation is not necessary for transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transitions (EMT) in mammary epithelial cells. PP1 directly inhibits TGF-beta receptors I and II.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 6;281(1):59-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503304200. Epub 2005 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16267045
-
EMT and TGF-beta in renal fibrosis.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010 Jan 1;2(1):229-38. doi: 10.2741/s60. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010. PMID: 20036943 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of cancer.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2009;85(8):314-23. doi: 10.2183/pjab.85.314. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19838011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways in TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:289243. doi: 10.1155/2012/289243. Epub 2012 Jan 29. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 22363839 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 Inhibits the Growth of Osteosarcoma and Attenuates Metastasis through the Wnt/β-Catenin and EMT Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jul 11;2020:6065124. doi: 10.1155/2020/6065124. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32733585 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the cAMP and Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway Increases Proliferation to Promote Re-Epithelialization of Human Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):925-37. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0247. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27112176 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in TGF beta1-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal epithelial cells are topologically related in the human interactome map.BMC Genomics. 2007 Oct 22;8:383. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-383. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17953753 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4: a novel signaling pathway during renal fibrogenesis.J Surg Res. 2011 Jun 1;168(1):e61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2009.09.053. Epub 2009 Oct 23. J Surg Res. 2011. PMID: 20089260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–791. - PubMed
-
- de Caestecker MP, Piek E, Roberts AB. Role of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:1388–1402. - PubMed
-
- Atfi A, Djelloul S, Chastre E, Davis R, Gespach C. Evidence for a role of Rho-like GTPases and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK) in transforming growth factor beta-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1429–1432. - PubMed
-
- Engel ME, McDonnell MA, Law BK, Moses HL. Interdependent SMAD and JNK signaling in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37413–37420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
