SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels
- PMID: 15527857
- PMCID: PMC7111769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.09.033
SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels
Abstract
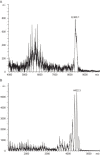
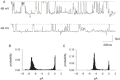
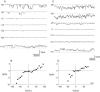
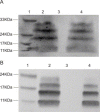
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) is caused by a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Coronaviruses including SARS-CoV encode an envelope (E) protein, a small, hydrophobic membrane protein. We report that, in planar lipid bilayers, synthetic peptides corresponding to the SARS-CoV E protein forms ion channels that are more permeable to monovalent cations than to monovalent anions. Affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies recognizing the N-terminal 19 residues of SARS-CoV E protein were used to establish the specificity of channel formation by inhibiting the ion currents generated in the presence of the E protein peptides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of the putative fusion peptide of the severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus spike protein.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):7195-206. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.7195-7206.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890958 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus E protein forms ion channels with functionally and structurally-involved membrane lipids.Virology. 2012 Oct 25;432(2):485-94. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Virology. 2012. PMID: 22832120 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of SARS-CoV E protein ion channel activity by tuning the protein and lipid charge.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Sep;1828(9):2026-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23688394 Free PMC article.
-
The spike protein of SARS-CoV--a target for vaccine and therapeutic development.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Mar;7(3):226-36. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2090. Epub 2009 Feb 9. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19198616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the accessory viral proteins unique to the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus.Antiviral Res. 2006 Nov;72(2):78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.05.010. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Antiviral Res. 2006. PMID: 16820226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane Activity and Viroporin Assembly for the SARS-CoV-2 E Protein Are Regulated by Cholesterol.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 26;14(9):1061. doi: 10.3390/biom14091061. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334828 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for the use of viral proteins for the construction of chimeric toxins.Arch Virol. 2024 Sep 26;169(10):208. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06139-8. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39327316 Review.
-
Transmembrane conformation of the envelope protein of an alpha coronavirus, NL63.Protein Sci. 2024 Apr;33(4):e4923. doi: 10.1002/pro.4923. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38501465 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Condensation and Curvature Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein.Langmuir. 2024 Feb 6;40(5):2646-2655. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c03079. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 38258382 Free PMC article.
-
Brownian Aging as One of the Mechanistic Components That Shape the Single-Channel Ionic Currents through Biological and Synthetic Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Nov 11;13(11):879. doi: 10.3390/membranes13110879. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker C.F., Oblatt-Montal M., Kochendoerfer G.G., Montal M. Chemical synthesis and single channel properties of tetrameric and pentameric TASP proteins derived from the transmembrane domain of HIV Virus protein u-Vpu. J. Biol. Chem. 2004:17483–17489. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

