BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 15523558
- PMCID: PMC524471
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020377
BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis
Abstract
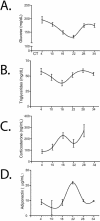
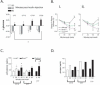
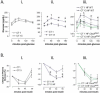
Circadian timing is generated through a unique series of autoregulatory interactions termed the molecular clock. Behavioral rhythms subject to the molecular clock are well characterized. We demonstrate a role for Bmal1 and Clock in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Inactivation of the known clock components Bmal1 (Mop3) and Clock suppress the diurnal variation in glucose and triglycerides. Gluconeogenesis is abolished by deletion of Bmal1 and is depressed in Clock mutants, but the counterregulatory response of corticosterone and glucagon to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia is retained. Furthermore, a high-fat diet modulates carbohydrate metabolism by amplifying circadian variation in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, and mutation of Clock restores the chow-fed phenotype. Bmal1 and Clock, genes that function in the core molecular clock, exert profound control over recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Furthermore, asynchronous dietary cues may modify glucose homeostasis via their interactions with peripheral molecular clocks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
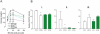
Similar articles
-
Dual role of the CLOCK/BMAL1 circadian complex in transcriptional regulation.FASEB J. 2006 Mar;20(3):530-2. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5321fje. Epub 2006 Jan 25. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16507766
-
Obesity alters circadian expressions of molecular clock genes in the brainstem.Brain Res. 2009 Mar 31;1263:58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.071. Epub 2009 Jan 15. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19401184
-
Clock mutation facilitates accumulation of cholesterol in the liver of mice fed a cholesterol and/or cholic acid diet.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jan;294(1):E120-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00061.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 30. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 17971517
-
Chromatin remodeling and circadian control: master regulator CLOCK is an enzyme.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:105-12. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.049. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419267 Review.
-
[Synchronization and genetic redundancy in circadian clocks].Med Sci (Paris). 2008 Mar;24(3):270-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2008243270. Med Sci (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18334175 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The impact of sleep disorders on glucose metabolism: endocrine and molecular mechanisms.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015 Mar 24;7:25. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0018-3. eCollection 2015. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015. PMID: 25834642 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose Clocks: Burning the Midnight Oil.J Biol Rhythms. 2015 Oct;30(5):364-73. doi: 10.1177/0748730415581234. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Biol Rhythms. 2015. PMID: 25926681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early nocturnal meal skipping alters the peripheral clock and increases lipogenesis in mice.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012 Sep 10;9(1):78. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-78. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22963033 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate-Dependent BMAL1 Regulation in Cultured Bergmann Glia Cells.Neurochem Res. 2015 May;40(5):961-70. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1551-z. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25749891
-
The functional significance of the skeletal muscle clock: lessons from Bmal1 knockout models.Skelet Muscle. 2016 Oct 13;6:33. doi: 10.1186/s13395-016-0107-5. eCollection 2016. Skelet Muscle. 2016. PMID: 27752300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhtar RA, Reddy AB, Maywood ES, Clayton JD, King VM, et al. Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Curr Biol. 2002;12:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht U, Eichele G. The mammalian circadian clock. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003;13:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Bergman RN, Ider YZ, Bowden CR, Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1979;236:E667–677. - PubMed
-
- Boston RC, Stefanovski D, Moate PJ, Sumner AE, Watanabe RM, et al. MINMOD millennium: A computer program to calculate glucose effectiveness and insulin sensitivity from the frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2003;5:1003–1015. - PubMed
-
- Brotman DJ, Girod JP. The metabolic syndrome: A tug-of-war with no winner. Cleve Clin J Med. 2002;69:990–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

