Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A regulates viral and cellular gene expression by modulation of the NF-kappaB transcription factor pathway
- PMID: 15498875
- PMCID: PMC524829
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402135101
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A regulates viral and cellular gene expression by modulation of the NF-kappaB transcription factor pathway
Abstract
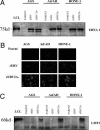
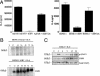
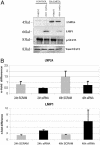
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated malignancies display distinct patterns of virus latent gene expression that reflect the complex interplay between the virus and its host cell. In the EBV-associated epithelial tumor nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), the virus-encoded latent membrane protein LMP2A is consistently expressed whereas the oncogenic LMP1 protein appears to be restricted to only a proportion of tumors. In an attempt to understand the contribution of LMP2A to the pathogenesis of NPC, we established carcinoma cell lines stably infected in vitro with either a wild-type recombinant EBV (rEBV) or a mutant rEBV in which LMP2A is deleted (rEBV-2A). An NPC-like pattern of EBV gene expression including LMP2A but not LMP1 was consistently observed in carcinoma cells infected with rEBV. However, carcinoma cells infected with rEBV-2A expressed high levels of LMP1 from the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-regulated L1-TR promoter. Consistent with this effect, basal STAT activity was reduced in rEBV-infected carcinoma cells, and this repression was relieved in the absence of LMP2A. This modulation of STAT activity correlated with the ability of LMP2A to inhibit the autocrine secretion of IL-6 from carcinoma cell lines. Exogenous IL-6 was able to induce expression of LMP1 by means of STAT3 activation both in rEBV-infected carcinoma cell lines and in the EBV-positive C666-1 NPC cell line. The LMP2A-mediated suppression of IL-6 was a consequence of NF-kappaB inhibition. These data reveal that LMP2A modulates two key transcription factor pathways in carcinoma cells and suggest that this finding may be important in the pathogenesis of EBV-associated tumors.
Figures
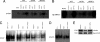
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 induces interleukin-8 through the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line.Laryngoscope. 2004 May;114(5):855-9. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200405000-00012. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 15126743
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6475-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27147748 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-type EBV infection induces tumorigenicity.Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 15;68(4):1030-6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5252. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18281477
-
Pathogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2013 Aug 28;337(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23689138 Review.
-
Role of Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 in the carcinogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Mol Immunol. 2007 Jun;4(3):185-96. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17601372 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Interactions between Two LMP2A PY Motifs of EBV and WW Domains of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase AIP4.Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;11(5):379. doi: 10.3390/life11050379. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922228 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma through disruption of PML nuclear bodies.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Oct 3;4(10):e1000170. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000170. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18833293 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies of Epstein-Barr virus to evade innate antiviral immunity of its human host.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 22;13:955603. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.955603. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35935191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The replication and transcription activator of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 cooperatively enhances cytokine-activated, STAT3-mediated gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 29;292(39):16257-16266. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.786970. Epub 2017 Aug 15. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28821622 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus: the mastermind of immune chaos.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1297994. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1297994. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38384471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rickinson, A. B. & Kieff, E. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M. (Lippincott, Philadelphia), pp. 2575-2627.
-
- Kieff, E. & Rickinson, A. B. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M. (Lippincott, Philadelphia), pp. 2511-2574.
-
- Young, L. S. & Murray, P. G. (2003) Oncogene 22, 5108-8121. - PubMed
-
- Raab-Traub, N. (2002) Semin. Cancer Biol. 12, 431-441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

