TI-VAMP/VAMP7 is required for optimal phagocytosis of opsonised particles in macrophages
- PMID: 15470500
- PMCID: PMC524391
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600427
TI-VAMP/VAMP7 is required for optimal phagocytosis of opsonised particles in macrophages
Abstract
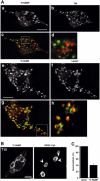
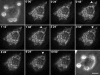
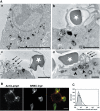
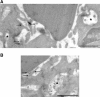
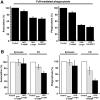
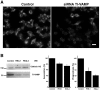
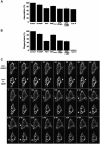
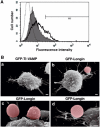
Phagocytosis relies on extension of plasmalemmal pseudopods generated by focal actin polymerisation and delivery of membranes from intracellular pools. Here we show that compartments of the late endocytic pathway, bearing the tetanus neurotoxin-insensitive vesicle-associated membrane protein (TI-VAMP/VAMP7), are recruited upon particle binding and undergo exocytosis before phagosome sealing in macrophages during Fc receptor (FcR)-mediated phagocytosis. Expression of the dominant-negative amino-terminal domain of TI-VAMP or depletion of TI-VAMP with small interfering RNAs inhibited phagocytosis mediated by Fc or complement receptors. In addition, inhibition of TI-VAMP activity led to a reduced exocytosis of late endocytic vesicles and this resulted in an early blockade of pseudopod extension, as observed by scanning electron microscopy. Therefore, TI-VAMP defines a new pathway of membrane delivery required for optimal FcR-mediated phagocytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ADP ribosylation factor 6 is activated and controls membrane delivery during phagocytosis in macrophages.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jun 23;161(6):1143-50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200210069. Epub 2003 Jun 16. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12810696 Free PMC article.
-
A dual mechanism controlling the localization and function of exocytic v-SNAREs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 22;100(15):9011-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1431910100. Epub 2003 Jul 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12853575 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Longin domain of TI-VAMP impairs lysosomal secretion and epithelial cell migration.Biol Cell. 2007 May;99(5):261-71. doi: 10.1042/BC20060097. Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17288539
-
The tetanus neurotoxin-sensitive and insensitive routes to and from the plasma membrane: fast and slow pathways?Traffic. 2005 May;6(5):366-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00288.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 15813747 Review.
-
Phagosome dynamics and function.Bioessays. 2000 Mar;22(3):255-63. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(200003)22:3<255::AID-BIES7>3.0.CO;2-R. Bioessays. 2000. PMID: 10684585 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel function for SNAP29 (synaptosomal-associated protein of 29 kDa) in mast cell phagocytosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049886. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185475 Free PMC article.
-
SNX3 recruits to phagosomes and negatively regulates phagocytosis in dendritic cells.Immunology. 2013 May;139(1):30-47. doi: 10.1111/imm.12051. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23237080 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ and synaptotagmin VII-dependent delivery of lysosomal membrane to nascent phagosomes.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 25;174(7):997-1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605004. Epub 2006 Sep 18. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16982801 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleoside diphosphate kinase NDK-1/NME1 promotes phagocytosis in concert with DYN-1/Dynamin.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):11606-11614. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900220R. Epub 2019 Jul 17. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31242766 Free PMC article.
-
Transport of the major myelin proteolipid protein is directed by VAMP3 and VAMP7.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 13;31(15):5659-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6638-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21490207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aderem A, Underhill DM (1999) Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol 17: 593–623 - PubMed
-
- Advani RJ, Bae HR, Bock JB, Chao DS, Doung YC, Prekeris R, Yoo JS, Scheller RH (1998) Seven novel mammalian SNARE proteins localize to distinct membrane compartments. J Biol Chem 273: 10317–10324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

