Retrotransposition-Competent Human LINE-1 Induces Apoptosis in Cancer Cells With Intact p53
- PMID: 15467158
- PMCID: PMC555774
- DOI: 10.1155/S1110724304403131
Retrotransposition-Competent Human LINE-1 Induces Apoptosis in Cancer Cells With Intact p53
Abstract
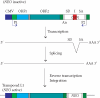
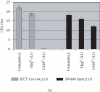
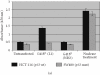
Retrotransposition of human LINE-1 (L1) element, a major representative non-LTR retrotransposon in the human genome, is known to be a source of insertional mutagenesis. However, nothing is known about effects of L1 retrotransposition on cell growth and differentiation. To investigate the potential for such biological effects and the impact that human L1 retrotransposition has upon cancer cell growth, we examined a panel of human L1 transformed cell lines following a complete retrotransposition process. The results demonstrated that transposition of L1 leads to the activation of the p53-mediated apoptotic pathway in human cancer cells that possess a wild-type p53. In addition, we found that inactivation of p53 in cells, where L1 was undergoing retrotransposition, inhibited the induction of apoptosis. This suggests an association between active retrotransposition and a competent p53 response in which induction of apoptosis is a major outcome. These data are consistent with a model in which human retrotransposition is sensed by the cell as a "genetic damaging event" and that massive retrotransposition triggers signaling pathways resulting in apoptosis.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Human LINE-1 retrotransposon induces DNA damage and apoptosis in cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2006 May 2;6:13. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-6-13. Cancer Cell Int. 2006. PMID: 16670018 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Capsaicin.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 19;19(10):3243. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103243. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347711 Free PMC article.
-
VL30 retrotransposition signals activation of a caspase-independent and p53-dependent death pathway associated with mitochondrial and lysosomal damage.Cell Res. 2010 May;20(5):553-62. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.48. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20386572
-
Guardian of the Human Genome: Host Defense Mechanisms against LINE-1 Retrotransposition.Front Chem. 2016 Jun 28;4:28. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2016.00028. eCollection 2016. Front Chem. 2016. PMID: 27446907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Transcriptional Control of LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Cellular Host Factors in Somatic Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Mar 7;4:14. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00014. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27014690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A new human embryonic cell type associated with activity of young transposable elements allows definition of the inner cell mass.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jun 20;21(6):e3002162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002162. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37339119 Free PMC article.
-
HERV-K and LINE-1 DNA Methylation and Reexpression in Urothelial Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2013 Sep 26;3:255. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00255. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24133654 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting retrotransposons: a review.Mob DNA. 2016 Aug 11;7:16. doi: 10.1186/s13100-016-0070-z. eCollection 2016. Mob DNA. 2016. PMID: 27525044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human LINE-1 retrotransposon creates DNA double-strand breaks.J Mol Biol. 2006 Apr 14;357(5):1383-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.089. Epub 2006 Feb 9. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16490214 Free PMC article.
-
The curious case of APOBEC3 activation by cancer-associated human papillomaviruses.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jan 11;14(1):e1006717. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006717. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29324878 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hutchison C.A, Hardies S.C, Loeb D.D, Shehee W.R, Edgell M.H. LINEs and related retroposons: long interspersed repeated sequences in the eucaryotic genome. In: Berg D.E, Howe M.M, editors. Mobile DNA. Washington, DC, Wash: ASM Press; 1989. pp. 593–617.
-
- Boeke J.D, Stoye J.P. Retrotransposons, endogenous retroviruses, and the evolution of retroelements. In: Coffin J.M, Hughes S.H, Varmus H.E, editors. Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. pp. 343–435. - PubMed
-
- Fanning T.G, Singer M.F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;910(3):203–212. - PubMed
-
- Moran J.V, Gilbert N. Mammalian LINE-1 retrotransposons and related elements. In: Craig N, Craigie R, Gellert M, et al., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC, Wash: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 836–869.
-
- Smit A.F, Toth G, Riggs A.D, Jurka J. Ancestral, mammalian-wide subfamilies of LINE-1 repetitive sequences. J Mol Biol. 1995;246(3):401–417. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

