A dynamic transcriptional network communicates growth potential to ribosome synthesis and critical cell size
- PMID: 15466158
- PMCID: PMC529537
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1228804
A dynamic transcriptional network communicates growth potential to ribosome synthesis and critical cell size
Abstract
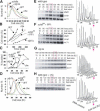
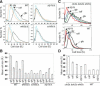
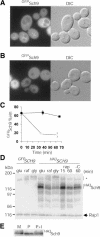
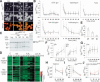
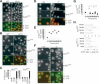
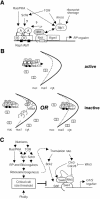
Cell-size homeostasis entails a fundamental balance between growth and division. The budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae establishes this balance by enforcing growth to a critical cell size prior to cell cycle commitment (Start) in late G1 phase. Nutrients modulate the critical size threshold, such that cells are large in rich medium and small in poor medium. Here, we show that two potent negative regulators of Start, Sfp1 and Sch9, are activators of the ribosomal protein (RP) and ribosome biogenesis (Ribi) regulons, the transcriptional programs that dictate ribosome synthesis rate in accord with environmental and intracellular conditions. Sfp1 and Sch9 are required for carbon-source modulation of cell size and are regulated at the level of nuclear localization and abundance, respectively. Sfp1 nuclear concentration responds rapidly to nutrient and stress conditions and is regulated by the Ras/PKA and TOR signaling pathways. In turn, Sfp1 influences the nuclear localization of Fhl1 and Ifh1, which bind to RP gene promoters. Starvation or the absence of Sfp1 causes Fhl1 and Ifh1 to localize to nucleolar regions, concomitant with reduced RP gene transcription. These findings suggest that nutrient signals set the critical cell-size threshold via Sfp1 and Sch9-mediated control of ribosome biosynthetic rates.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Rab escort protein integrates the secretion system with TOR signaling and ribosome biogenesis.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 15;23(16):1944-58. doi: 10.1101/gad.1804409. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684114 Free PMC article.
-
Sfp1 interaction with TORC1 and Mrs6 reveals feedback regulation on TOR signaling.Mol Cell. 2009 Mar 27;33(6):704-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.034. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19328065
-
TOR regulates ribosomal protein gene expression via PKA and the Forkhead transcription factor FHL1.Cell. 2004 Dec 29;119(7):969-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.047. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15620355
-
Transcriptional control of ribosome biogenesis in yeast: links to growth and stress signals.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Aug 27;49(4):1589-1599. doi: 10.1042/BST20201136. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34240738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple roles of the general regulatory factor Abf1 in yeast ribosome biogenesis.Curr Genet. 2017 Feb;63(1):65-68. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0621-3. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27262581 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolutionary rewiring of the ribosomal protein transcription pathway modifies the interaction of transcription factor heteromer Ifh1-Fhl1 (interacts with forkhead 1-forkhead-like 1) with the DNA-binding specificity element.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17508-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.436683. Epub 2013 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23625919 Free PMC article.
-
The critical size is set at a single-cell level by growth rate to attain homeostasis and adaptation.Nat Commun. 2012;3:1012. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2015. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22910358
-
Cell volume homeostatically controls the rDNA repeat copy number and rRNA synthesis rate in yeast.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 7;17(4):e1009520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009520. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33826644 Free PMC article.
-
Sch9 partially mediates TORC1 signaling to control ribosomal RNA synthesis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Dec 15;8(24):4085-90. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.24.10170. Epub 2009 Dec 25. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19823048 Free PMC article.
-
The F-box protein Dia2 overcomes replication impedance to promote genome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1709-27. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.057836. Epub 2006 Jun 4. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16751663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baroni M.D., Monti, P., and Alberghina, L. 1994. Repression of growth-regulated G1 cyclin expression by cyclic AMP in budding yeast. Nature 371: 339-342. - PubMed
-
- Beer M.A. and Tavazoie, S. 2004. Predicting gene expression from sequence. Cell 117: 185-198. - PubMed
-
- Bishop A.C., Ubersax, J.A., Petsch, D.T., Matheos, D.P., Gray, N.S., Blethrow, J. Shimizu, E., Tsien, J.Z., Schultz, P.G., Rose, M.D., et al. 2000. A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature 407: 395-401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
