Estrogen-related receptor alpha directs peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling in the transcriptional control of energy metabolism in cardiac and skeletal muscle
- PMID: 15456881
- PMCID: PMC517878
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9079-9091.2004
Estrogen-related receptor alpha directs peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling in the transcriptional control of energy metabolism in cardiac and skeletal muscle
Abstract
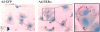
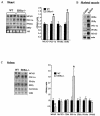
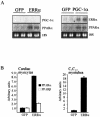
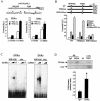
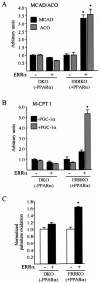
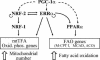
Estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) are orphan nuclear receptors activated by the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha), a critical regulator of cellular energy metabolism. However, metabolic target genes downstream of ERRalpha have not been well defined. To identify ERRalpha-regulated pathways in tissues with high energy demand such as the heart, gene expression profiling was performed with primary neonatal cardiac myocytes overexpressing ERRalpha. ERRalpha upregulated a subset of PGC-1alpha target genes involved in multiple energy production pathways, including cellular fatty acid transport, mitochondrial and peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation, and mitochondrial respiration. These results were validated by independent analyses in cardiac myocytes, C2C12 myotubes, and cardiac and skeletal muscle of ERRalpha-/- mice. Consistent with the gene expression results, ERRalpha increased myocyte lipid accumulation and fatty acid oxidation rates. Many of the genes regulated by ERRalpha are known targets for the nuclear receptor PPARalpha, and therefore, the interaction between these regulatory pathways was explored. ERRalpha activated PPARalpha gene expression via direct binding of ERRalpha to the PPARalpha gene promoter. Furthermore, in fibroblasts null for PPARalpha and ERRalpha, the ability of ERRalpha to activate several PPARalpha targets and to increase cellular fatty acid oxidation rates was abolished. PGC-1alpha was also shown to activate ERRalpha gene expression. We conclude that ERRalpha serves as a critical nodal point in the regulatory circuitry downstream of PGC-1alpha to direct the transcription of genes involved in mitochondrial energy-producing pathways in cardiac and skeletal muscle.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PGC-1alpha coactivates PDK4 gene expression via the orphan nuclear receptor ERRalpha: a mechanism for transcriptional control of muscle glucose metabolism.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):10684-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10684-10694.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314495 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl3 interacts cooperatively with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) coactivator 1alpha to coactivate nuclear receptors estrogen-related receptor alpha and PPARalpha.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;29(15):4091-102. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01669-08. Epub 2009 May 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19451226 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) and gamma (ERRgamma) on the regulation of ERRalpha gene expression.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007 Jan 29;264(1-2):128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17157980 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor signaling and cardiac energetics.Circ Res. 2004 Sep 17;95(6):568-78. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000141774.29937.e3. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15375023 Review.
-
[Transcriptional regulation of metabolic switching PDK4 gene under various physiological conditions].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Jan;127(1):153-62. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.127.153. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17202796 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Targeting ERRα promotes cytotoxic effects against acute myeloid leukemia through suppressing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Oct 26;15(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01372-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36289517 Free PMC article.
-
Complex interplay between the lipin 1 and the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 α (HNF4α) pathways to regulate liver lipid metabolism.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051320. Epub 2012 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236470 Free PMC article.
-
Pellino1 deficiency reprograms cardiomyocytes energy metabolism in lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial dysfunction.Amino Acids. 2021 May;53(5):713-737. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02978-w. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33885999 Free PMC article.
-
ERRα: unraveling its role as a key player in cell migration.Oncogene. 2024 Feb;43(6):379-387. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02899-w. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38129506 Review.
-
Calcineurin A and CaMKIV transactivate PGC-1alpha promoter, but differentially regulate cytochrome c promoter in rat skeletal muscle.Pflugers Arch. 2007 May;454(2):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0206-6. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17273866
References
-
- Barger, P. M., A. C. Browning, A. N. Garner, and D. P. Kelly. 2001. p38 MAP kinase activates PPARα: a potential role in the cardiac metabolic stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 276:44495-44501. - PubMed
-
- Bernal-Mizrachi, C., S. Weng, C. Feng, B. N. Finck, R. H. Knutsen, T. C. Leone, T. Coleman, R. P. Mecham, D. P. Kelly, and C. F. Semenkovich. 2003. Glucocorticoid induction of hypertension and diabetes is PPAR-α dependent in mice. Nat. Med. 9:1069-1075. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, J., F. Djouadi, and D. P. Kelly. 1998. Fatty acids activate transcription of the muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I gene in cardiac myocytes via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23786-23792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
