Cyclin A and cyclin D1 as significant prognostic markers in colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 15385053
- PMCID: PMC524166
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-4-22
Cyclin A and cyclin D1 as significant prognostic markers in colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer is a common cancer all over the world. Aberrations in the cell cycle checkpoints have been shown to be of prognostic significance in colorectal cancer.
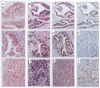
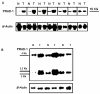
Methods: The expression of cyclin D1, cyclin A, histone H3 and Ki-67 was examined in 60 colorectal cancer cases for co-regulation and impact on overall survival using immunohistochemistry, southern blot and in situ hybridization techniques. Immunoreactivity was evaluated semi quantitatively by determining the staining index of the studied proteins.
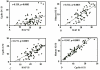
Results: There was a significant correlation between cyclin D1 gene amplification and protein overexpression (concordance = 63.6%) and between Ki-67 and the other studied proteins. The staining index for Ki-67, cyclin A and D1 was higher in large, poorly differentiated tumors. The staining index of cyclin D1 was significantly higher in cases with deeply invasive tumors and nodal metastasis. Overexpression of cyclin A and D1 and amplification of cyclin D1 were associated with reduced overall survival. Multivariate analysis shows that cyclin D1 and A are two independent prognostic factors in colorectal cancer patients.
Conclusions: Loss of cell cycle checkpoints control is common in colorectal cancer. Cyclin A and D1 are superior independent indicators of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Therefore, they may help in predicting the clinical outcome of those patients on an individual basis and could be considered important therapeutic targets.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel immunohistochemical method to estimate cell-cycle phase distribution in archival tissue: implications for the prediction of outcome in colorectal cancer.J Pathol. 2003 Oct;201(2):187-97. doi: 10.1002/path.1444. J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14517835
-
Expression patterns of cyclins D1, E and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21waf1/cip1, p27kip1 in colorectal carcinoma: correlation with other cell cycle regulators (pRb, p53 and Ki-67 and PCNA) and clinicopathological features.Int J Clin Pract. 2008 Nov;62(11):1736-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01105.x. Int J Clin Pract. 2008. PMID: 19143860
-
Cyclin D1 overexpression in primary hypopharyngeal carcinomas.Cancer. 1996 Aug 1;78(3):390-5. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960801)78:3<390::AID-CNCR2>3.0.CO;2-O. Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8697381
-
Expression of cyclin D1, but not cyclins E and A, is related to progression in bilharzial bladder cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 1997 Dec;3(12 Pt 1):2247-51. Clin Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9815621
-
The impact of cell proliferation markers and p53 mutation status on prognosis of non-metastatic colon cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2014 Jun;109(7):665-75. doi: 10.1002/jso.23563. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24464927
Cited by
-
The role of Pygo2 for Wnt/ß-catenin signaling activity during intestinal tumor initiation and progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80612-80632. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13016. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27811361 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated risk of colorectal cancer associated with the AA genotype of the cyclin D1 A870G polymorphism in an Indian population.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006 Mar;132(3):193-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-005-0039-7. Epub 2005 Dec 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16328437
-
Radiation promotes colorectal cancer initiation and progression by inducing senescence-associated inflammatory responses.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 30;35(26):3365-75. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.395. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26477319 Free PMC article.
-
Network Topologies Decoding Cervical Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 26;10(8):e0135183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135183. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26308848 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual impact of adipocytes and colorectal cancer cells growing in co-culture conditions.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun 14;21(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01155-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37316878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang GL, Huang S. Adenovirus expressing RIZ1 in tumor suppressor gene therapy of microsatellite unstable colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1796–1798. - PubMed
-
- Soliman AS, Bondy ML, Levin B, Hamza MR, Ismail K, Ismail S, Hammam HM, El-Hattab O, Kamal SM, Soliman AG, Dorgham LA, McPherson RS, Beasley RP. Colorectal cancer in Egyptian patients under 40 years of age. Int J Cancer. 1997;71:26–30. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19970328)71:1<26::AID-IJC6>3.0.CO;2-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soliman AS, Bondy ML, Guan Y, El-Badawy S, Mokhtar N, Bayomi S, Raouf AA, Ismail S, McPherson RS, Abdel-Hakim TF, Beasley PR, Levin B, Wei Q. Reduced expression of mismatch repair genes in colorectal cancer patients in Egypt. Int J Oncol. 1998;12:1315–1319. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

