MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 15372072
- PMCID: PMC524334
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385
MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
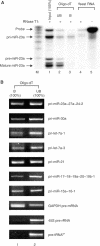
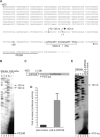
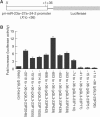
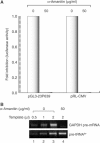
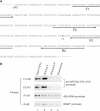
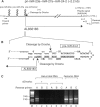
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) constitute a large family of noncoding RNAs that function as guide molecules in diverse gene silencing pathways. Current efforts are focused on the regulatory function of miRNAs, while little is known about how these unusual genes themselves are regulated. Here we present the first direct evidence that miRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II (pol II). The primary miRNA transcripts (pri-miRNAs) contain cap structures as well as poly(A) tails, which are the unique properties of class II gene transcripts. The treatment of human cells with alpha-amanitin decreased the level of pri-miRNAs at a concentration that selectively inhibits pol II activity. Furthermore, chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses show that pol II is physically associated with a miRNA promoter. We also describe, for the first time, the detailed structure of a miRNA gene by determining the promoter and the terminator of mir-23a approximately 27a approximately 24-2. These data indicate that pol II is the main, if not the only, RNA polymerase for miRNA gene transcription. Our study offers a basis for understanding the structure and regulation of miRNA genes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional gene silencing by siRNAs and miRNAs.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Jun;15(3):331-41. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.05.006. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 15925505 Review.
-
Use of RNA polymerase II to transcribe artificial microRNAs.Methods Enzymol. 2005;392:371-80. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)92022-8. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 15644193
-
In vitro analysis of microRNA processing using recombinant Dicer and cytoplasmic extracts of HeLa cells.Methods. 2007 Oct;43(2):105-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.04.005. Methods. 2007. PMID: 17889796
-
Using synthetic precursor and inhibitor miRNAs to understand miRNA function.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;419:289-301. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-033-1_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369991
-
Gene silencing in vitro and in vivo using intronic microRNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:295-312. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:295. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957384 Review.
Cited by
-
Stage-specific expression patterns and co-targeting relationships among miRNAs in the developing mouse cerebral cortex.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 22;7(1):1366. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07092-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39433948 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 16;12:1470875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1470875. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39479511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Biliary Tract Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 23;17(5):791. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050791. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27223281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and regulatory effects of microRNA-182 in osteosarcoma cells: A pilot study.Oncol Lett. 2016 May;11(5):3040-3048. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4375. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27123060 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the non-coding RNAs in Alzheimer's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(21):3543-59. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1125-z. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22955374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2002) Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell 110: 55–67 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ (2001) Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363–366 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

