Multivesicular body-ESCRT components function in pH response regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans
- PMID: 15371534
- PMCID: PMC532031
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0666
Multivesicular body-ESCRT components function in pH response regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans
Abstract
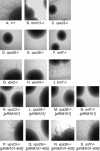
The ESCRT-I, -II, and -III protein complexes function to create multivesicular bodies (MVBs) for sorting of proteins destined for the lysosome or vacuole. Prior studies with Saccharomyces cerevisiae have shown that the ESCRT-III protein Snf7p interacts with the MVB pathway protein Bro1p as well as its homolog Rim20p. Rim20p has no role in MVB formation, but functions in the Rim101p pH-response pathway; Rim20p interacts with transcription factor Rim101p and is required for the activation of Rim101p by C-terminal proteolytic cleavage. We report here that ESCRT-III proteins Snf7p and Vps20p as well as all ESCRT-I and -II proteins are required for Rim101p proteolytic activation in S. cerevisiae. Mutational analysis indicates that the Rim20p N-terminal region interacts with Snf7p, and an insertion in the Rim20p "Bro1 domain" abolishes this interaction, as determined with two-hybrid assays. Disruption of the MVB pathway through mutations affecting non-ESCRT proteins does not impair Rim101p processing. The relationship between the MVB pathway and Rim101p pathway is conserved in Candida albicans, because mutations in four ESCRT subunit genes abolish alkaline pH-induced filamentation, a phenotype previously seen for rim101 and rim20 mutants. The defect is suppressed by expression of C-terminally truncated Rim101-405p, as expected for mutations that block Rim101p proteolytic activation. These results indicate that the ESCRT complexes govern a specific signal transduction pathway and suggest that the MVB pathway may provide a signal that regulates pH-responsive transcription.
Figures
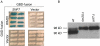
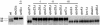


Similar articles
-
Relationship of DFG16 to the Rim101p pH response pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 May;4(5):890-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.5.890-899.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15879523 Free PMC article.
-
Snf7p, a component of the ESCRT-III protein complex, is an upstream member of the RIM101 pathway in Candida albicans.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Dec;3(6):1609-18. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.6.1609-1618.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15590834 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast PalA/AIP1/Alix homolog Rim20p associates with a PEST-like region and is required for its proteolytic cleavage.J Bacteriol. 2001 Dec;183(23):6917-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.23.6917-6923.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11698381 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to environmental pH in Candida albicans and its relation to pathogenesis.Curr Genet. 2003 Oct;44(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0415-2. Epub 2003 Jun 18. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 12819929 Review.
-
The signaling mechanism of ambient pH sensing and adaptation in yeast and fungi.FEBS J. 2012 Apr;279(8):1407-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08548.x. Epub 2012 Mar 23. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22360598 Review.
Cited by
-
The RIM101 signal transduction pathway regulates Candida albicans virulence during experimental keratomycosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Sep;51(9):4668-76. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4726. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20375342 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of the ESCRT machinery to a putative seven-transmembrane-domain receptor is mediated by an arrestin-related protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;30(4):897-907. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00132-09. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20028738 Free PMC article.
-
Split-ubiquitin two-hybrid assay to analyze protein-protein interactions at the endosome: application to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Bro1 interacting with ESCRT complexes, the Doa4 ubiquitin hydrolase, and the Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Aug;6(8):1266-77. doi: 10.1128/EC.00024-07. Epub 2007 May 18. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17513562 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium chloride sensitivity connects the activity of PEX11 and RIM20 to the translation of PGM2 and other mRNAs with structured 5'-UTRs.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Nov;477(11):2643-2656. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04466-5. Epub 2022 May 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35598219
-
ALIX-CHMP4 interactions in the human ESCRT pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 3;105(22):7687-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801567105. Epub 2008 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18511562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babst, M., Katzmann, D.J., Estepa-Sabal, E.J., Meerloo, T., and Emr, S.D. (2002a). Escrt-III: an endosome-associated heterooligomeric protein complex required for mvb sorting. Dev. Cell 3, 271-282. - PubMed
-
- Babst, M., Katzmann, D.J., Snyder, W.B., Wendland, B., and Emr, S.D. (2002b). Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell 3, 283-289. - PubMed
-
- Bilodeau, P.S., Urbanowski, J.L., Winistorfer, S.C., and Piper, R.C. (2002). The Vps27p Hse1p complex binds ubiquitin and mediates endosomal protein sorting. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 534-539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

