Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases
- PMID: 15367757
- PMCID: PMC2828947
- DOI: 10.1126/stke.2502004re13
Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases
Abstract
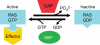
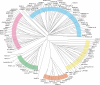
The tumor oncoproteins HRAS, KRAS, and NRAS are the founding members of a larger family of at least 35 related human proteins. Using a somewhat broader definition of sequence similarity reveals a more extended superfamily of more than 170 RAS-related proteins. The RAS superfamily of GTP (guanosine triphosphate) hydrolysis-coupled signal transduction relay proteins can be subclassified into RAS, RHO, RAB, and ARF families, as well as the closely related Galpha family. The members of each family can, in turn, be arranged into evolutionarily conserved branches. These groupings reflect structural, biochemical, and functional conservation. Recent findings have provided insights into the signaling characteristics of representative members of most RAS superfamily branches. The analysis presented here may serve as a guide for predicting the function of numerous uncharacterized superfamily members. Also described are guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) distinct from members of the RAS superfamily. These related proteins employ GTP binding and GTPase domains in diverse structural contexts, expanding the scope of their function in humans.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A guide to low molecular weight GTPases.Cell Growth Differ. 1990 May;1(5):251-8. Cell Growth Differ. 1990. PMID: 2150754 Review. No abstract available.
-
A yeast GTPase-activating protein that interacts specifically with a member of the Ypt/Rab family.Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):736-9. doi: 10.1038/361736a0. Nature. 1993. PMID: 8441469
-
Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives.Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643-54. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. Nature. 1993. PMID: 8259209 Review.
-
Regulators and effectors of ras proteins.Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:601-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003125. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1667084 Review. No abstract available.
-
A requirement for wild-type Ras isoforms in mutant KRas-driven signalling and transformation.Biochem J. 2013 Jun 1;452(2):313-20. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121578. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23496764
Cited by
-
Effect of Slit/Robo signaling on regeneration in lung emphysema.Exp Mol Med. 2021 May;53(5):986-992. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00633-8. Epub 2021 May 25. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34035465 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of mutations in SNP loci of K-RAS, hMLH1 and hMSH2 genes in neoplastic intestinal polyps and colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 28;20(48):18338-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18338. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25561800 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction properties of the human Rab GTPase family--comparative analysis reveals determinants of molecular binding selectivity.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034870. Epub 2012 Apr 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22523562 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the catalytic domain of the Salmonella virulence factor SseI.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012 Dec;68(Pt 12):1613-21. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912039042. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012. PMID: 23151626 Free PMC article.
-
PRUNE1 and NME/NDPK family proteins influence energy metabolism and signaling in cancer metastases.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Jun;43(2):755-775. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10165-4. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38180572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
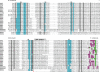
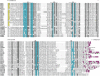
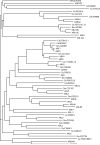
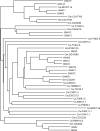
- Human Genome Nomenclature Committee All prediced proteins discussed in this review are supported by both genomic and cDNA sequences. (HGNC, http://www.gene.ucl.ac.uk/nomenclature) symbols are used throughout (Table 1 provides a list of some common gene names corresponding to HGNC symbols)
-
-
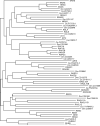
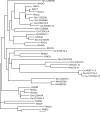
ClustalW was used for all sequence alignments and for the generation of dendrograms. Only GTPase domains were used in the analysis (i.e., extraneous sequences were removed).
-
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: Conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991;349:117–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
