Targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): a new approach to treating cancer
- PMID: 15365568
- PMCID: PMC2409926
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602162
Targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): a new approach to treating cancer
Abstract
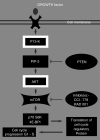
mTOR is a downstream mediator in the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway, which plays a critical role in regulating basic cellular functions. These include cell proliferation, survival, mobility and angiogenesis. Rapamycin and its analogues (CCI-779, RAD001 and AP23573) have specific antagonistic action on the function of mTOR. This leads to inhibition of the downstream signalling elements and results in the cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. This group of drugs may have a place in Oncology for the treatment of cancers, which occur as a result of increased activity of the PI3 kinase/Akt/m-TOR pathway. The basic structure of the pathway was reviewed in this article, together with results of the clinical studies targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. This is an exciting area for development and poses many challenges to researchers.
Similar articles
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin: a new molecular target for breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2003 Jun;4(2):126-37. doi: 10.3816/cbc.2003.n.018. Clin Breast Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12864941 Review.
-
Current status and challenges associated with targeting mTOR for cancer therapy.BioDrugs. 2009;23(2):77-91. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200923020-00002. BioDrugs. 2009. PMID: 19489650 Review.
-
New targets for therapy in breast cancer: mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) antagonists.Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6(5):219-24. doi: 10.1186/bcr927. Epub 2004 Aug 12. Breast Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15318929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) kinase pathway: its role in tumourigenesis and targeted antitumour therapy.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2005;10(3):479-98. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16217558 Review.
-
Therapeutic targets: MTOR and related pathways.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Sep;5(9):1065-73. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.9.3175. Epub 2006 Sep 6. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16969122 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin E succinate induces apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in EC109 esophageal cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Aug;14(2):1531-7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5445. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27357907 Free PMC article.
-
Natural small-molecule enhancers of autophagy induce autophagic cell death in apoptosis-defective cells.Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 1;4:5510. doi: 10.1038/srep05510. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24981420 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine Inhibits the Proliferation of Human Gastric Carcinoma Cells by Retarding Akt/mTOR/p70S6K Signaling.J Cancer. 2014 Apr 24;5(5):382-9. doi: 10.7150/jca.8024. eCollection 2014. J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24799956 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin Eye Drops Suppress Lacrimal Gland Inflammation In a Murine Model of Sjögren's Syndrome.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Jan 1;58(1):372-385. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19159. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28122086 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of the microRNA transcriptome mediates resistance to rapamycin.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 1;288(9):6034-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.416446. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23300087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham RT, Wiederrecht GJ (1996) Immunopharmacology of rapamycin. Annu Rev Immunol 14: 483–510 - PubMed
-
- Alexandre J, Raymond E, Depenbrock H (1999) CCI-779, a new rapamycin analog, has antitumour activity at doses inducing only mild cutaneous effects and mucositis: early results of an ongoing phase 1 study. Proceedings of the AACR/NCI/EORTC International Conference on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics. Washington, DC, November 16–19
-
- Aronica SM, Katzellenbogen B (1991) Progestrogene receptor regulation in uterine cells: stimulation by oestrogen, cyclic adenosine 3,5-monophosphate, and insulin like growth factor I and suppression by antioestrogens and protein kinase inhibitors. Endocrinology 128: 2045–2052 - PubMed
-
- Atkin MB, Hidalgo M, Stadler W, Logan T, Dutcher JP, Hudes G, Park Y, Marshall B, Boni J, Dukart G (2002) A randomises phase 2 study of intravenous CCI-779 administered weekly to patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Meeting Proceedings American Society of Clinical Oncology: vol 21: Poster Presentation Abst 36
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous