Population history and natural selection shape patterns of genetic variation in 132 genes
- PMID: 15361935
- PMCID: PMC515367
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020286
Population history and natural selection shape patterns of genetic variation in 132 genes
Abstract
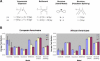
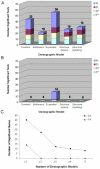
Identifying regions of the human genome that have been targets of natural selection will provide important insights into human evolutionary history and may facilitate the identification of complex disease genes. Although the signature that natural selection imparts on DNA sequence variation is difficult to disentangle from the effects of neutral processes such as population demographic history, selective and demographic forces can be distinguished by analyzing multiple loci dispersed throughout the genome. We studied the molecular evolution of 132 genes by comprehensively resequencing them in 24 African-Americans and 23 European-Americans. We developed a rigorous computational approach for taking into account multiple hypothesis tests and demographic history and found that while many apparent selective events can instead be explained by demography, there is also strong evidence for positive or balancing selection at eight genes in the European-American population, but none in the African-American population. Our results suggest that the migration of modern humans out of Africa into new environments was accompanied by genetic adaptations to emergent selective forces. In addition, a region containing four contiguous genes on Chromosome 7 showed striking evidence of a recent selective sweep in European-Americans. More generally, our results have important implications for mapping genes underlying complex human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disentangling the effects of demography and selection in human history.Mol Biol Evol. 2005 Jan;22(1):63-73. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh252. Epub 2004 Sep 8. Mol Biol Evol. 2005. PMID: 15356276
-
Assessing the evolutionary impact of amino acid mutations in the human genome.PLoS Genet. 2008 May 30;4(5):e1000083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000083. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18516229 Free PMC article.
-
Darwinian and demographic forces affecting human protein coding genes.Genome Res. 2009 May;19(5):838-49. doi: 10.1101/gr.088336.108. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19279335 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation and adaptation in Africa: implications for human evolution and disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jul 1;6(7):a008524. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008524. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 24984772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide scans for loci under selection in humans.Hum Genomics. 2005 Jun;2(2):113-25. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-2-2-113. Hum Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16004726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep sympatric mtDNA divergence in the autumnal moth (Epirrita autumnata).Ecol Evol. 2012 Jan;3(1):126-44. doi: 10.1002/ece3.434. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Ecol Evol. 2012. PMID: 23404314 Free PMC article.
-
Co-evolution of KIR2DL3 with HLA-C in a human population retaining minimal essential diversity of KIR and HLA class I ligands.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 3;106(44):18692-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906051106. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19837691 Free PMC article.
-
Demographic history differences between Hispanics and Brazilians imprint haplotype features.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 6;12(7):jkac111. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac111. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35511163 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling the false-positive rate in multilocus genome scans for selection.Genetics. 2007 Feb;175(2):737-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064642. Epub 2006 Nov 16. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17110489 Free PMC article.
-
Positive selection can create false hotspots of recombination.Genetics. 2006 Mar;172(3):2011-4. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.052183. Epub 2005 Dec 30. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16387873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akey JM, Zhang K, Xiong M, Jin L. The effect of single nucleotide polymorphism identification strategies on estimates of linkage disequilibrium. Mol Biol Evol. 2003;20:232–242. - PubMed
-
- Andolfatto P. Adaptive hitchhiking effects on genome variability. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:635–641. - PubMed
-
- Cavalli-Sforza LL. Population structure and human evolution. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966;164:362–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

