Sfp1 is a stress- and nutrient-sensitive regulator of ribosomal protein gene expression
- PMID: 15353587
- PMCID: PMC521938
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0405353101
Sfp1 is a stress- and nutrient-sensitive regulator of ribosomal protein gene expression
Abstract
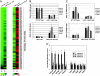
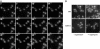
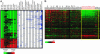
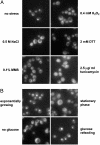
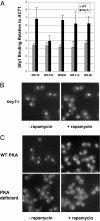
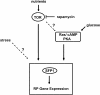
Yeast cells modulate their protein synthesis capacity in response to physiological needs through the transcriptional control of ribosomal protein (RP) genes. Here we demonstrate that the transcription factor Sfp1, previously shown to play a role in the control of cell size, regulates RP gene expression in response to nutrients and stress. Under optimal growth conditions, Sfp1 is localized to the nucleus, bound to the promoters of RP genes, and helps promote RP gene expression. In response to inhibition of target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling, stress, or changes in nutrient availability, Sfp1 is released from RP gene promoters and leaves the nucleus, and RP gene transcription is down-regulated. Additionally, cells lacking Sfp1 fail to appropriately modulate RP gene expression in response to environmental cues. We conclude that Sfp1 integrates information from nutrient- and stress-responsive signaling pathways to help control RP gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TOR regulates ribosomal protein gene expression via PKA and the Forkhead transcription factor FHL1.Cell. 2004 Dec 29;119(7):969-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.047. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15620355
-
Sfp1 interaction with TORC1 and Mrs6 reveals feedback regulation on TOR signaling.Mol Cell. 2009 Mar 27;33(6):704-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.034. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19328065
-
A Rab escort protein integrates the secretion system with TOR signaling and ribosome biogenesis.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 15;23(16):1944-58. doi: 10.1101/gad.1804409. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684114 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of the general regulatory factor Abf1 in yeast ribosome biogenesis.Curr Genet. 2017 Feb;63(1):65-68. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0621-3. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27262581 Review.
-
Identification of TOR signaling complexes: more TORC for the cell growth engine.Cell. 2002 Oct 4;111(1):9-12. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01009-7. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12372295 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional control of growth and development in yeast.Genetics. 2012 Sep;192(1):73-105. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.135731. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22964838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curated collection of yeast transcription factor DNA binding specificity data reveals novel structural and gene regulatory insights.Genome Biol. 2011 Dec 21;12(12):R125. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-12-r125. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22189060 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Specialization and Codon Preference of Lignocellulolytic Genes in the White Rot Basidiomycete Ceriporiopsis subvermispora.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;11(10):1227. doi: 10.3390/genes11101227. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092062 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Mar;70(1):253-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.70.1.253-282.2006. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16524925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth control of the eukaryote cell: a systems biology study in yeast.J Biol. 2007;6(2):4. doi: 10.1186/jbiol54. J Biol. 2007. PMID: 17439666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

