Yeast actin patches are networks of branched actin filaments
- PMID: 15337772
- PMCID: PMC2172413
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200404159
Yeast actin patches are networks of branched actin filaments
Abstract
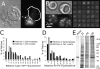
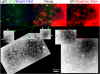
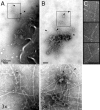
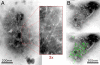
Cortical actin patches are the most prominent actin structure in budding and fission yeast. Patches assemble, move, and disassemble rapidly. We investigated the mechanisms underlying patch actin assembly and motility by studying actin filament ultrastructure within a patch. Actin patches were partially purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and examined by negative-stain electron microscopy (EM). To identify patches in the EM, we correlated fluorescence and EM images of GFP-labeled patches. Patches contained a network of actin filaments with branches characteristic of Arp2/3 complex. An average patch contained 85 filaments. The average filament was only 50-nm (20 actin subunits) long, and the filament to branch ratio was 3:1. Patches lacking Sac6/fimbrin were unstable, and patches lacking capping protein were relatively normal. Our results are consistent with Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerization driving yeast actin patch assembly and motility, as described by a variation of the dendritic nucleation model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanical stiffness of reconstituted actin patches correlates tightly with endocytosis efficiency.PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 25;17(10):e3000500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000500. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31652255 Free PMC article.
-
Arp2/3 ATP hydrolysis-catalysed branch dissociation is critical for endocytic force generation.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;8(8):826-33. doi: 10.1038/ncb1443. Epub 2006 Jul 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16862144
-
Role of formins in actin assembly: nucleation and barbed-end association.Science. 2002 Jul 26;297(5581):612-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1072309. Epub 2002 Jun 6. Science. 2002. PMID: 12052901
-
Abp1p and cortactin, new "hand-holds" for actin.J Cell Biol. 2001 Aug 20;154(4):679-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105061. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11514584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The yeast actin cytoskeleton: from cellular function to biochemical mechanism.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Sep;70(3):605-45. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00013-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16959963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions of WASp, myosin-I, and verprolin with Arp2/3 complex during actin patch assembly in fission yeast.J Cell Biol. 2005 Aug 15;170(4):637-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200502053. Epub 2005 Aug 8. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16087707 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Arp2 and Arp3 nucleotide-binding pocket mutations on Arp2/3 complex function.J Cell Biol. 2005 Jan 17;168(2):315-28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200408177. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657399 Free PMC article.
-
Central roles of small GTPases in the development of cell polarity in yeast and beyond.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Mar;71(1):48-96. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00028-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17347519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulling-force generation by ensembles of polymerizing actin filaments.Phys Biol. 2019 Dec 13;17(1):016005. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/ab59bd. Phys Biol. 2019. PMID: 31747656 Free PMC article.
-
Competition between Tropomyosin, Fimbrin, and ADF/Cofilin drives their sorting to distinct actin filament networks.Elife. 2017 Mar 10;6:e23152. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23152. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28282023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchoin, L., K.J. Amann, H.N. Higgs, J.B. Marchand, D.A. Kaiser, and T.D. Pollard. 2000. Direct observation of dendritic actin filament networks nucleated by Arp2/3 complex and WASP/Scar proteins. Nature. 404:1007–1011. - PubMed
-
- Cameron, L.A., T.M. Svitkina, D. Vignjevic, J.A. Theriot, and G.G. Borisy. 2001. Dendritic organization of actin comet tails. Curr. Biol. 11:130–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

