Expression profiling of serum inducible genes identifies a subset of SRF target genes that are MKL dependent
- PMID: 15329155
- PMCID: PMC516031
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-13
Expression profiling of serum inducible genes identifies a subset of SRF target genes that are MKL dependent
Abstract
Background: Serum Response Factor (SRF) is a transcription factor that is required for the expression of many genes including immediate early genes, cytoskeletal genes, and muscle-specific genes. SRF is activated in response to extra-cellular signals by its association with a diverse set of co-activators in different cell types. In the case of the ubiquitously expressed immediate early genes, the two sets of SRF binding proteins that regulate its activity are the TCF family of proteins that include Elk1, SAP1 and SAP2 and the myocardin-related MKL family of proteins that include MKL1 and MKL2 (also known as MAL, MRTF-A and -B and BSAC). In response to serum or growth factors these two classes of co-activators are activated by different upstream signal transduction pathways. However, it is not clear how they differentially activate SRF target genes.
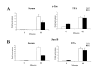
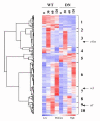
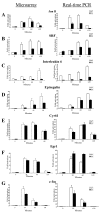
Results: In order to identify the serum-inducible SRF target genes that are specifically dependent on the MKL pathway, we have performed microarray experiments using a cell line that expresses dominant negative MKL1. This approach was used to identify SRF target genes whose activation is MKL-dependent. Twenty-eight of 150 serum-inducible genes were found to be MKL-dependent. The promoters of the serum-inducible genes were analyzed for SRF binding sites and other common regulatory elements. Putative SRF binding sites were found at a higher rate than in a mouse promoter database but were only identified in 12% of the serum-inducible promoters analyzed. Additional partial matches to the consensus SRF binding site were found at a higher than expected rate in the MKL-dependent gene promoters. The analysis for other common regulatory elements is discussed.
Conclusions: These results suggest that a subset of immediate early and SRF target genes are activated by the Rho-MKL pathway. MKL may also contribute to the induction of other SRF target genes however its role is not essential, possibly due to other activation mechanisms such as MAPK phosphorylation of TCFs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myocardin/MKL family of SRF coactivators: key regulators of immediate early and muscle specific gene expression.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Sep 1;93(1):74-82. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20199. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15352164 Review.
-
Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1, a potent transcriptional coactivator for serum response factor (SRF), is required for serum induction of SRF target genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Sep;23(18):6597-608. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6597-6608.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12944485 Free PMC article.
-
Megakaryoblastic leukemia-1/2, a transcriptional co-activator of serum response factor, is required for skeletal myogenic differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 24;278(43):41977-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305679200. Epub 2003 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14565952
-
Megakaryoblastic leukemia factor-1 transduces cytoskeletal signals and induces smooth muscle cell differentiation from undifferentiated embryonic stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17578-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400961200. Epub 2004 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14970199
-
Regulation of Dendritic Synaptic Morphology and Transcription by the SRF Cofactor MKL/MRTF.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 2;14:767842. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.767842. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34795561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Key Fibrogenic Signaling.Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015;3(2):183-192. doi: 10.1007/s40139-015-0077-z. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25973345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression signatures of site-specificity in cancer metastases.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Feb;37(1):159-171. doi: 10.1007/s10585-019-09995-w. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 31555944
-
Double null cells reveal that CBP and p300 are dispensable for p53 targets p21 and Mdm2 but variably required for target genes of other signaling pathways.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jan 15;10(2):212-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.2.14542. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21220944 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying functional single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human CArGome.Physiol Genomics. 2011 Sep 22;43(18):1038-48. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00098.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Physiol Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21771879 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in silico analysis identifies bona fide MyoD binding sites within the Myocyte stress 1 gene promoter.BMC Mol Biol. 2008 May 19;9:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-50. BMC Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18489770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990;1:47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

