p19Arf suppresses growth, progression, and metastasis of Hras-driven carcinomas through p53-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 15314658
- PMCID: PMC509304
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020242
p19Arf suppresses growth, progression, and metastasis of Hras-driven carcinomas through p53-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
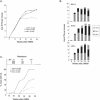
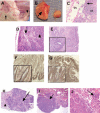
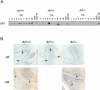
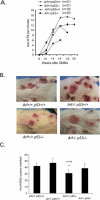
Ectopic expression of oncogenes such as Ras induces expression of p19(Arf), which, in turn, activates p53 and growth arrest. Here, we used a multistage model of squamous cell carcinoma development to investigate the functional interactions between Ras, p19(Arf), and p53 during tumor progression in the mouse. Skin tumors were induced in wild-type, p19(Arf)-deficient, and p53-deficient mice using the DMBA/TPA two-step protocol. Activating mutations in Hras were detected in all papillomas and carcinomas examined, regardless of genotype. Relative to wild-type mice, the growth rate of papillomas was greater in p19(Arf)-deficient mice, and reduced in p53-deficient mice. Malignant conversion of papillomas to squamous cell carcinomas, as well as metastasis to lymph nodes and lungs, was markedly accelerated in both p19 (Arf)- and p53-deficient mice. Thus, p19(Arf) inhibits the growth rate of tumors in a p53-independent manner. Through its regulation of p53, p19(Arf) also suppresses malignant conversion and metastasis. p53 expression was upregulated in papillomas from wild-type but not p19( Arf)-null mice, and p53 mutations were more frequently seen in wild-type than in p19( Arf)-null carcinomas. This indicates that selection for p53 mutations is a direct result of signaling from the initiating oncogenic lesion, Hras, acting through p19(Arf).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
p19/Arf and p53 suppress sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and carcinoma metastasis.Oncogene. 2008 May 15;27(22):3145-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210973. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18059331
-
Oncogenic ras activates the ARF-p53 pathway to suppress epithelial cell transformation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5025-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091100298. Epub 2001 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11309506 Free PMC article.
-
p19(ARF) is dispensable for oncogenic stress-induced p53-mediated apoptosis and tumor suppression in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):370-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.370-377.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739748 Free PMC article.
-
p53-Dependent and -independent functions of the Arf tumor suppressor.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:129-37. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2005.70.004. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. PMID: 16869746 Review.
-
Activation of p53 by oncogenes.Endocr Relat Cancer. 1999 Mar;6(1):45-8. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0060045. Endocr Relat Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10732786 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved domain in exon 2 coding for the human and murine ARF tumor suppressor protein is required for autophagy induction.Autophagy. 2013 Oct;9(10):1553-65. doi: 10.4161/auto.25831. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Autophagy. 2013. PMID: 23939042 Free PMC article.
-
ARF triggers cell G1 arrest by a P53 independent ERK pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Nov;357(1-2):415-22. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0912-4. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21660463
-
The Arf tumor suppressor protein inhibits Miz1 to suppress cell adhesion and induce apoptosis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Mar 22;188(6):905-18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200908103. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20308430 Free PMC article.
-
An ARF/CtBP2 complex regulates BH3-only gene expression and p53-independent apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2010 Mar;17(3):513-21. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.140. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 19798104 Free PMC article.
-
ARF induces autophagy by virtue of interaction with Bcl-xl.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 30;284(5):2803-2810. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804705200. Epub 2008 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19049976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birchmeier W, Weidner KM, Hulsken J, Behrens J. Molecular mechanisms leading to cell junction (cadherin) deficiency in invasive carcinomas. Cancer Biol. 1993;4:231–239. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: A review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Bremner R, Balmain A. Genetic changes in skin tumour progression: Correlation between presence of a mutant ras gene and loss of heterozygosity on mouse chromosome 7. Cell. 1990;61:407–417. - PubMed
-
- Buchmann A, Ruggeri B, Klein-Szanto AJP, Balmain A. Progression of squamous carcinoma cells to spindle carcinomas of mouse skin is associated with an imbalance of H-ras alleles on chromosome 7. Cancer Res. 1991;51:4097–4101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

