Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced arteriogenesis reduces energy failure in hemodynamic stroke
- PMID: 15306685
- PMCID: PMC514662
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404880101
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced arteriogenesis reduces energy failure in hemodynamic stroke
Abstract
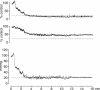
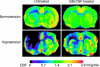
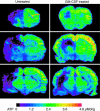
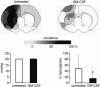
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is a powerful arteriogenic factor in the hypoperfused rat brain. To test the pathophysiological relevance of this response, the influence of GM-CSF on brain energy state was investigated in a model of hemodynamic stroke. Sprague-Dawley rats were submitted to three-vessel (bilateral vertebral and unilateral common carotid artery) occlusion (3-VO) to induce unilaterally accentuated brain hypoperfusion. One week later, hemodynamic stroke was induced by additional lowering of arterial blood pressure. Experiments were terminated by in situ freezing of the brain. ATP was measured in cryostat sections by using a bioluminescence method. The use of 3-VO, in combination with 15 min of hypotension of 50, 40, or 30 mmHg, did not produce disturbances of energy metabolism, however, focal areas of ATP depletion were unilaterally detected after 3-VO, in combination with 15 min of hypotension of 20 mmHg. Treating such animals with GM-CSF (40 microg.kg(-1).d(-1)) during the 1-week interval between 3-VO and induced hypotension significantly reduced the hemispheric volume of energy depletion from 48.8 +/- 44.2% (untreated group, n = 10) to 15.8 +/- 17.4% (treated group, n = 8, P = 0.033). GM-CSF-induced arteriogenesis is another approach to protect the brain against ischemic injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic induction of arteriogenesis in hypoperfused rat brain via granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.Circulation. 2003 Aug 5;108(5):610-5. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000074209.17561.99. Epub 2003 Jun 30. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12835229
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced vessel growth restores cerebral blood supply after bilateral carotid artery occlusion.Stroke. 2007 Apr;38(4):1320-8. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000259707.43496.71. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Stroke. 2007. PMID: 17332468
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as an arteriogenic factor in the treatment of ischaemic stroke.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005 Dec;5(12):1547-56. doi: 10.1517/14712598.5.12.1547. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16318419 Review.
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor improves cerebrovascular reserve capacity by enhancing collateral growth in the circle of Willis.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33(5):419-29. doi: 10.1159/000335869. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 22456527
-
[Therapeutically induced arteriogenesis in the brain. A new approach for the prevention of cerebral ischemia with vascular stenosis].Nervenarzt. 2006 Feb;77(2):215-20. doi: 10.1007/s00115-005-1988-4. Nervenarzt. 2006. PMID: 16273341 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The hematopoietic factor GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) promotes neuronal differentiation of adult neural stem cells in vitro.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Oct 22;8:88. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-88. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17953750 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term external counterpulsation augments cerebral blood flow and tissue oxygenation in chronic cerebrovascular occlusive disease.Eur J Neurol. 2018 Nov;25(11):1326-1332. doi: 10.1111/ene.13725. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Eur J Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29924461 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The innate immune system stimulating cytokine GM-CSF improves learning/memory and interneuron and astrocyte brain pathology in Dp16 Down syndrome mice and improves learning/memory in wild-type mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Jun 15;168:105694. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105694. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 35307513 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor α-subunit in the adult human brain with specific reference to Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012 Nov;119(11):1389-406. doi: 10.1007/s00702-012-0794-y. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012. PMID: 22430742
-
Growth factors in ischemic stroke.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Aug;15(8):1645-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00987.x. Epub 2009 Dec 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20015202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Busch, H. J., Buschmann, I. R., Mies, G., Bode, C. & Hossmann, K.-A. (2003) J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 23, 621-628. - PubMed
-
- Buschmann, I. R., Hoefer, I. E., van Royen, N., Katzer, E., Braun-Dulleaus, R., Heil, M., Kostin, S., Bode, C. & Schaper, W. (2001) Atherosclerosis 159, 343-356. - PubMed
-
- Ito, W. D., Arras, M., Winkler, B., Scholz, D., Schaper, J. & Schaper, W. (1997) Circ. Res. 80, 829-837. - PubMed
-
- Banai, S., Jaklitsch, M. T., Casscells, W., Shou, M., Shrivastav, S., Correa, R., Epstein, S. E. & Unger, E. F. (1991) Circ. Res. 69, 76-85. - PubMed
-
- Lazarous, D. F., Unger, E. F., Epstein, S. E., Stine, A., Arevalo, J. L., Chew, E. Y. & Quyyumi, A. A. (2000) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36, 1239-1244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

